Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2025; 31(10): 103133
Published online Mar 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i10.103133
Published online Mar 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i10.103133
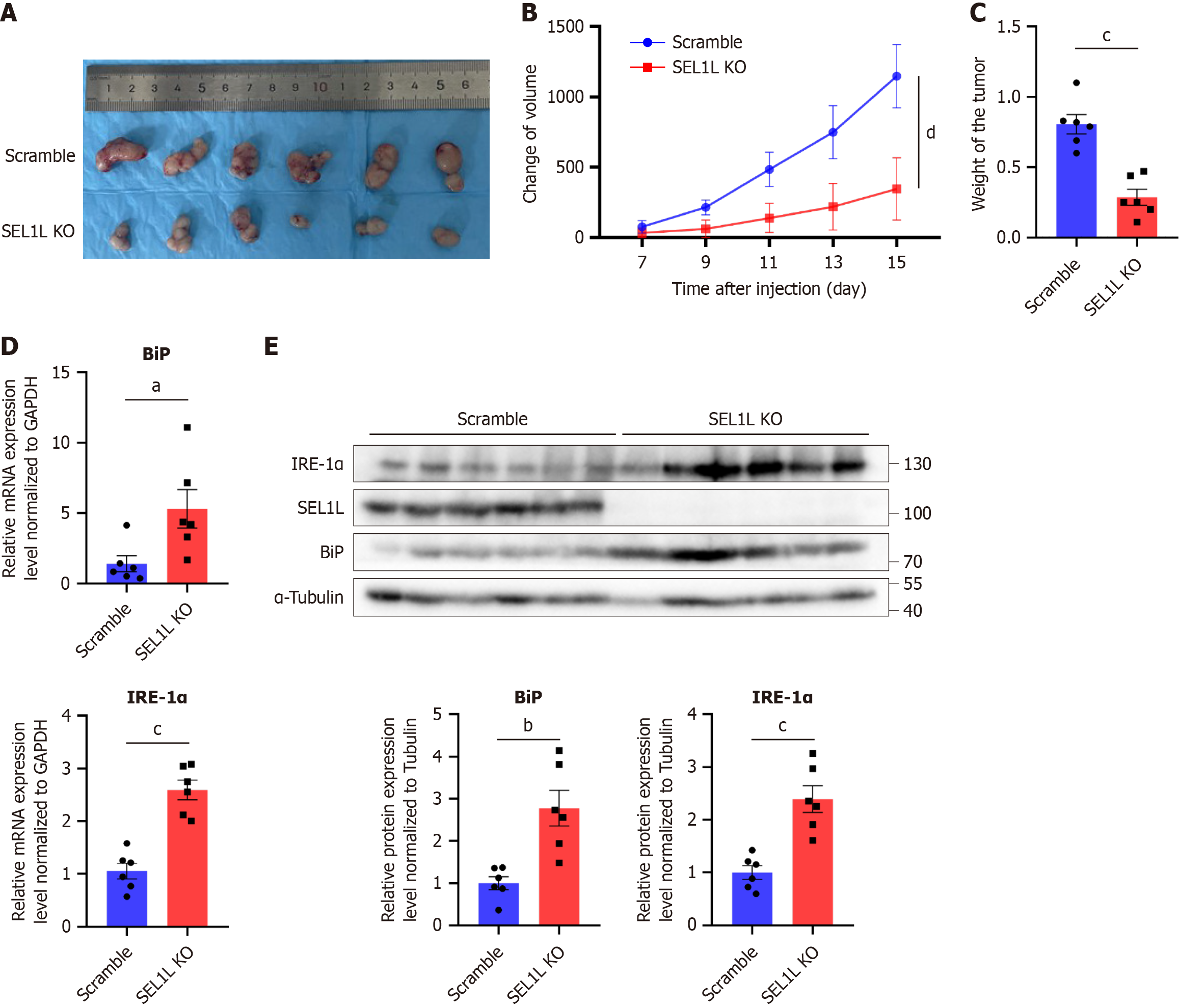
Figure 4 SEL1L knockout affected the tumor growth in vivo.
A: Subcutaneous xenografts dissected from mice at the endpoint; B: Subcutaneous tumor growth curves in nude mice (n = 6); C: Subcutaneous xenograft weights from mice at the endpoint; D: The mRNA expression of heavy-chain binding protein (BiP) and inositol-requiring enzyme (IRE)-1α was detected by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Each point represents a single sample; E: The protein expression of BiP and IRE-1α in the SEL1L knockout group was compared with the scramble group. aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. cP < 0.001. dP < 0.0001. GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; BiP: Heavy-chain binding protein; IRE-1α: Inositol-requiring enzyme-1α; KO: Knockout.
- Citation: Chen JN, Wang L, He YX, Sun XW, Cheng LJ, Li YN, Yoshida S, Shen ZY. SEL1L-mediated endoplasmic reticulum associated degradation inhibition suppresses proliferation and migration in Huh7 hepatocellular carcinoma cells. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(10): 103133
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i10/103133.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i10.103133