Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2025; 31(10): 101014
Published online Mar 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i10.101014
Published online Mar 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i10.101014
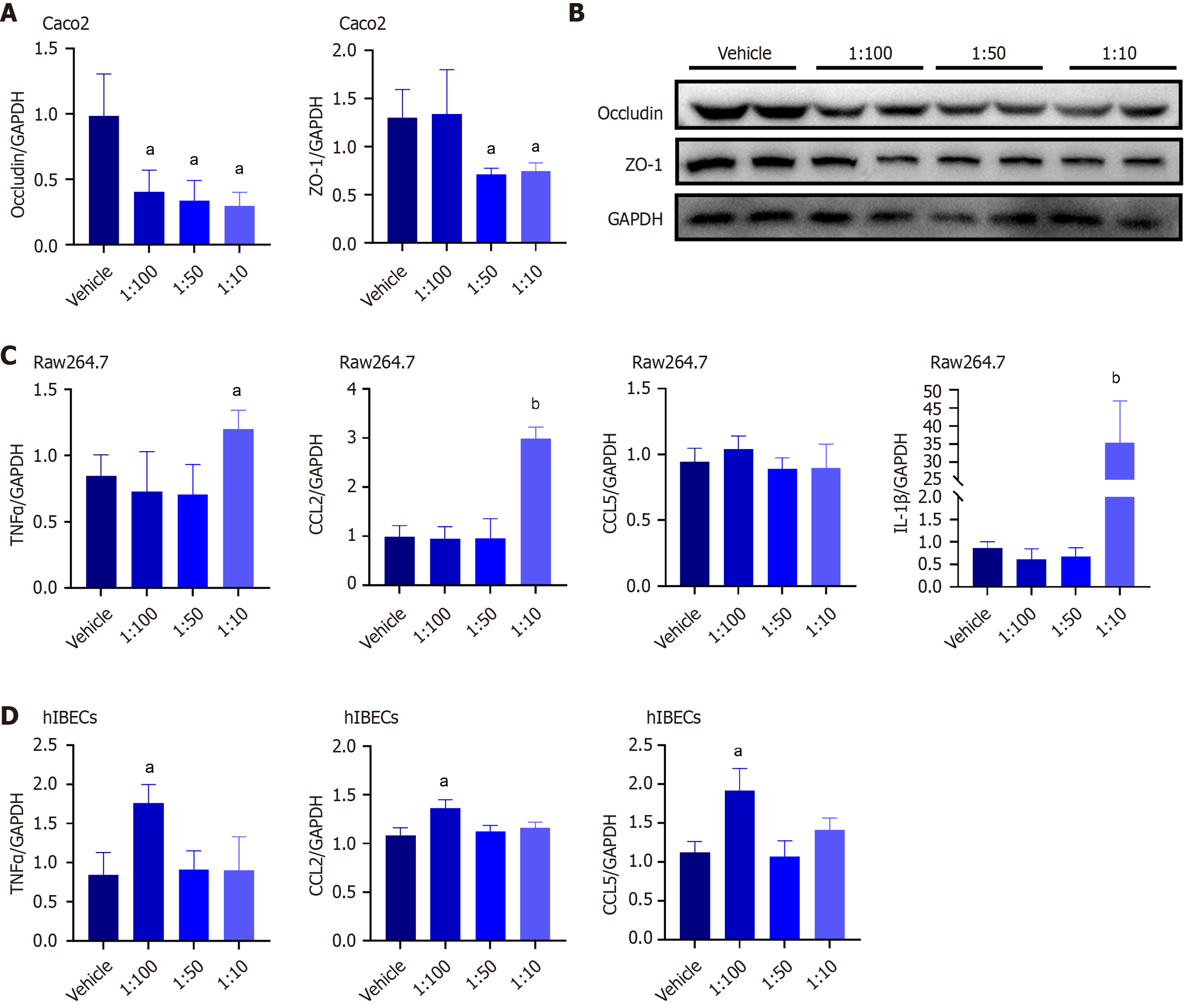
Figure 5 Ligilactobacillus murinus induces barrier injury and inflammatory activation in vitro.
A: Occludin and zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) mRNA levels in human intestinal epithelial Caco-2 cells; B: Protein ZO-1 and occludin protein levels in Caco-2 cells analyzed using western blotting. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase served as the loading control; C and D: Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα), CCL2, CCL5 and interleukin-1β mRNA levels in RAW264.7 cells (C) and TNFα, CCL2 and CCL5 mRNA levels in human intrahepatic bile duct epithelial cells (D) exposed at different concentrations of Lactococcus garvieae culture supernatants (1:100, 1:50, 1:10). All values are expressed as the mean ± SD; aP < 0.05 vs vehicle group; bP < 0.01 vs vehicle group; ZO-1: Zonula occludens-1; TNFα: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; IL: Interleukin; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
- Citation: Liu M, Ji YL, Hu YJ, Su YX, Yang J, Wang XY, Chu HY, Zhang X, Dong SJ, Yang H, Liu YH, Zhou SM, Guo LP, Ran Y, Li YN, Zhao JW, Zhang ZG, Piao MY, Zhou L. Lactococcus garvieae aggravates cholestatic liver disease by increasing intestinal permeability and enhancing bile acid reabsorption. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(10): 101014
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i10/101014.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i10.101014