Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2025; 31(1): 98561
Published online Jan 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i1.98561
Published online Jan 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i1.98561
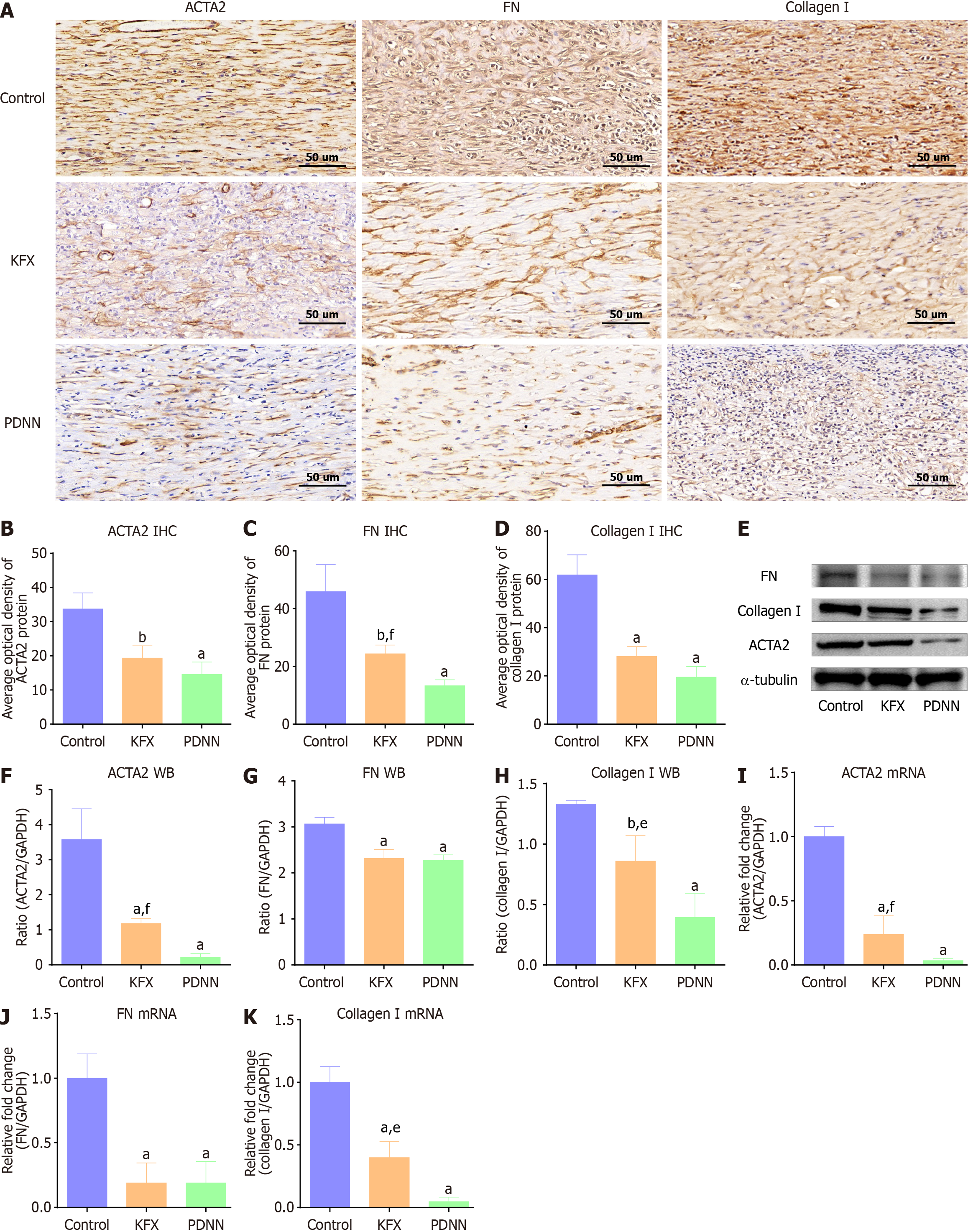
Figure 3 Kangfuxin solution inhibited the excessive deposition of fibrous components in artificial esophageal ulcers.
A: Representative images of immunohistochemical staining to detect Α-smooth muscle actin-2 (ACTA2), fibronectin (FN), and collagen I in the artificial ulcer of esophageal tissue, magnification 200 × (n = 4); B-D: Quantitation of the staining intensity of ACTA2, FN, and collagen I in (A) (n = 4); Kangfuxin solution (KFX) treatment reduced the distribution of ACTA2-positive myofibroblasts and suppressed the expression of extracellular matrix components FN and collagen I; E: The protein levels of ACTA2, FN, and collagen I were determined by western blot; α-tubulin was used as the loading control (n = 4); F-H: Quantitation of relative expression of ACTA2, FN, and collagen I in (E), respectively (n = 4); I-K: The mRNA levels of ACTA2, FN, and collagen I were quantitated by RT-PCR (n = 4); administration of KFX significantly suppressed the protein and gene expression of ACTA2, FN, and collagen I. Data are presented as mean ± SE. aP < 0.001 vs the control group, bP < 0.01 vs the control group, eP < 0.01 vs the PDNN group, fP < 0.05 vs the PDNN group. KFX: Kangfuxin solution; PDNN: Prednisolone; ACTA2: Α-smooth muscle actin-2; FN: Fibronectin; IHC: Immunohistochemistry; WB: Western blotting.
- Citation: Zhou X, Ma D, He YX, Jin J, Wang HL, Wang YF, Yang F, Liu JQ, Chen J, Li Z. Kangfuxin solution alleviates esophageal stenosis after endoscopic submucosal dissection: A natural ingredient strategy. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(1): 98561
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i1/98561.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i1.98561