Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2024; 30(9): 1177-1188
Published online Mar 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i9.1177
Published online Mar 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i9.1177
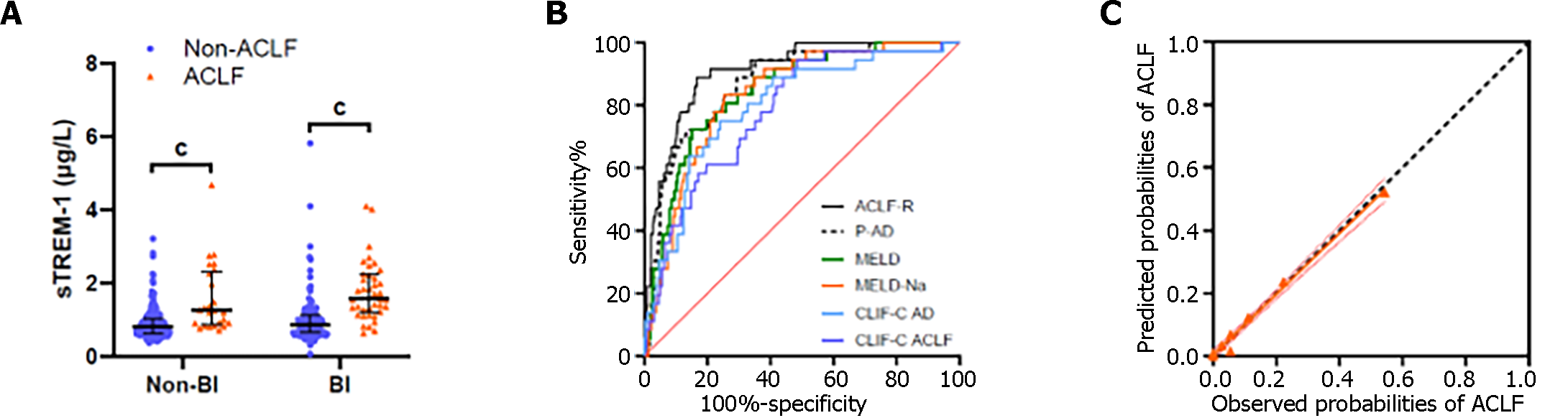
Figure 3 Acute-on-chronic liver failure risk score associated with acute-on-chronic liver failure development in cirrhosis with acute decompensation.
A: In bacterial infections (BI) or non-BI group, Soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cell-1 Levels at admission were higher in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) than those without; B: Prediction development of ACLF during 28-d follow-up for patients with acute decompensation according to ACLF risk score (ACLF-R) and other models; C: Calibration plot comparing the observed and predicted probabilities of ACLF from the Kaplan-Meier and ACLF-R. cP < 0.001. sTREM-1: Soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cell-1; ACLF: Acute-on-chronic liver failure score; BI: Bacterial infections; ACLF-R: Acute-on-chronic liver failure risk score; P-AD: Prognostic model of acute decompensation; MELD: Model for end-stage liver disease; CLIF-C: Chronic liver failure-consortium; CLIF-C AD: Chronic liver failure-consortium acute decompensation score; CLIF-C ACLF: Chronic liver failure-consortium acute-on-chronic liver failure score.
- Citation: Yu SM, Li H, Deng GH, Wang XB, Zheng X, Chen JJ, Meng ZJ, Zheng YB, Gao YH, Qian ZP, Liu F, Lu XB, Shi Y, Shang J, Chen RC, Huang Y. sTREM-1 as promising prognostic biomarker for acute-on-chronic liver failure and mortality in patients with acute decompensation of cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(9): 1177-1188
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i9/1177.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i9.1177