Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2024; 30(9): 1073-1095
Published online Mar 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i9.1073
Published online Mar 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i9.1073
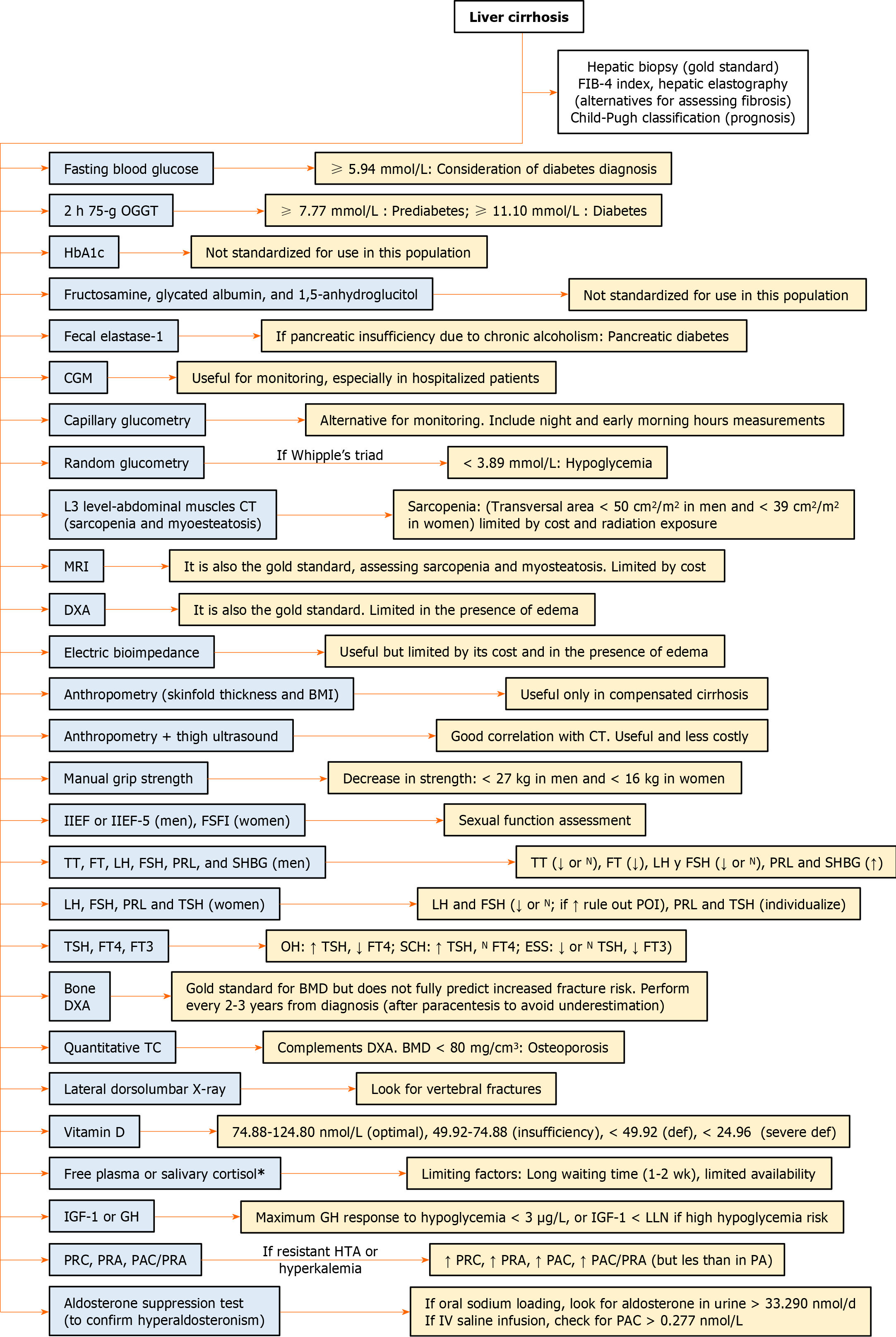
Figure 2 Summary of diagnostic tests used in the approach to endocrinopathies associated with liver cirrhosis.
The asterisk (*) represents that adrenal insufficiency should be evaluated if there is refractory hypotension, sodium less than 125 mmol/L, and high-density lipoproteins less than 0.39 mmol/L. BMD: Bone mineral density; BMI: Body mass index; CGM: Continuous glucose monitoring; CT: Computed tomography; DXA: Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry; FIB-4 index: Fibrosis-4 index; FSFI: Female Sexual Function Index; FSH: Follicle-stimulating hormone; FT: Free testosterone; GH: Growth hormone; HbA1c: Hemoglobin A1c; IGF-1: Insulin-like growth factor 1; IIEF: International Index of Erectile Function; IV: Intravenous; L3: 3rd lumbar vertebrae; LH: Luteinizing hormone; LLN: Lower limit of normality; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; OGGT: Oral glucose tolerance test; PA: Primary aldosteronism; PAC: Plasma aldosterone concentration; POI: Primary ovarian insufficiency; PRA: Plasma renin activity; PRC: Plasma renin concentration; PRL: Prolactin; SHBG: Sex hormone-binding globulin; TSH: Thyroid-stimulating hormone; TT: Total testosterone.
- Citation: Quiroz-Aldave JE, Gamarra-Osorio ER, Durand-Vásquez MDC, Rafael-Robles LDP, Gonzáles-Yovera JG, Quispe-Flores MA, Concepción-Urteaga LA, Román-González A, Paz-Ibarra J, Concepción-Zavaleta MJ. From liver to hormones: The endocrine consequences of cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(9): 1073-1095
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i9/1073.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i9.1073