Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2024; 30(9): 1043-1072
Published online Mar 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i9.1043
Published online Mar 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i9.1043
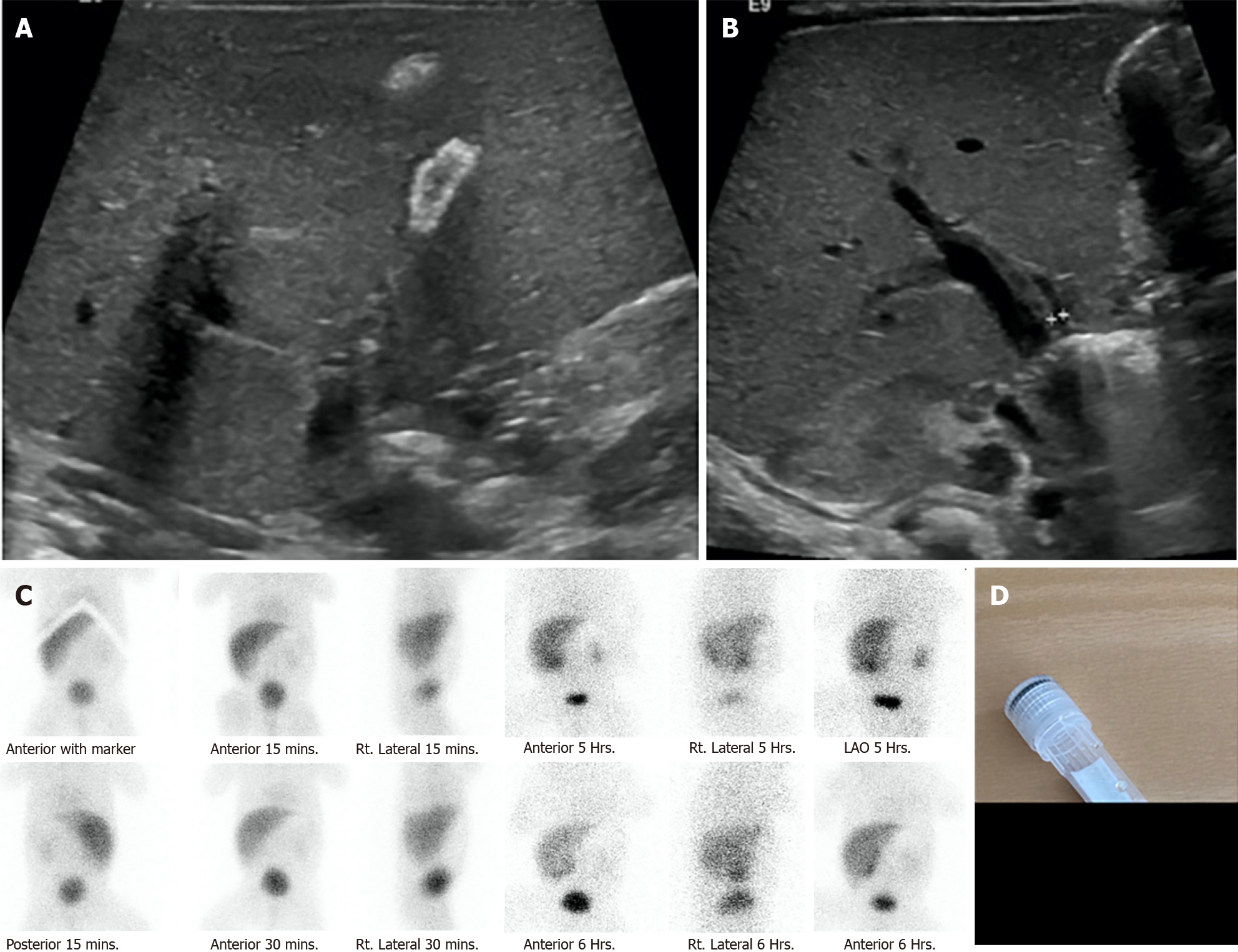
Figure 10 A 29-wk preterm newborn with neonatal sepsis, stage IIA necrotizing enterocolitis, bronchopulmonary dysplasia on the endotracheal tube, and prolonged total parenteral nutrition.
He had obvious jaundice and pale stool at 1 month of age. Liver function test showed total bilirubin (TB)/direct bilirubin (DB) values of 8.7/4.6 mg/dL, aspartate aminotransferase of 132, alanine aminotransferase of 52, alkaline phosphatase of 447 U/L, and albumin of 2.8 mg/dL. Intraoperative cholangiography was performed after 3 months of and showed a patent bile duct but the formation of large stone. The histopathology of liver biopsy revealed giant cell transformation with cholestasis in the bile canaliculi and hepatocytes, bile ductopenia, and absence of significant fibrosis. He underwent an eye examination by an ophthalmologist who found the posterior embryotoxon at the inferior of the eyes. The trio-exome showed a NOTCH2 mutation. After stone removal, TB and DB dramatically decreased to normal level in 7 d. A: Ultrasonography showing a small gallbladder with a diffused calcified wall; B: Ultrasonography showing non-dilatation of the intrahepatic or common bile duct (only 3 mm); C: Technetium-99m di-isopropyl iminodiacetic acid shows faint radiotracer excretion into the gastrointestinal tract; D: Gross stone specimen.
- Citation: Eiamkulbutr S, Tubjareon C, Sanpavat A, Phewplung T, Srisan N, Sintusek P. Diseases of bile duct in children. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(9): 1043-1072
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i9/1043.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i9.1043