Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2024; 30(8): 919-942
Published online Feb 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i8.919
Published online Feb 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i8.919
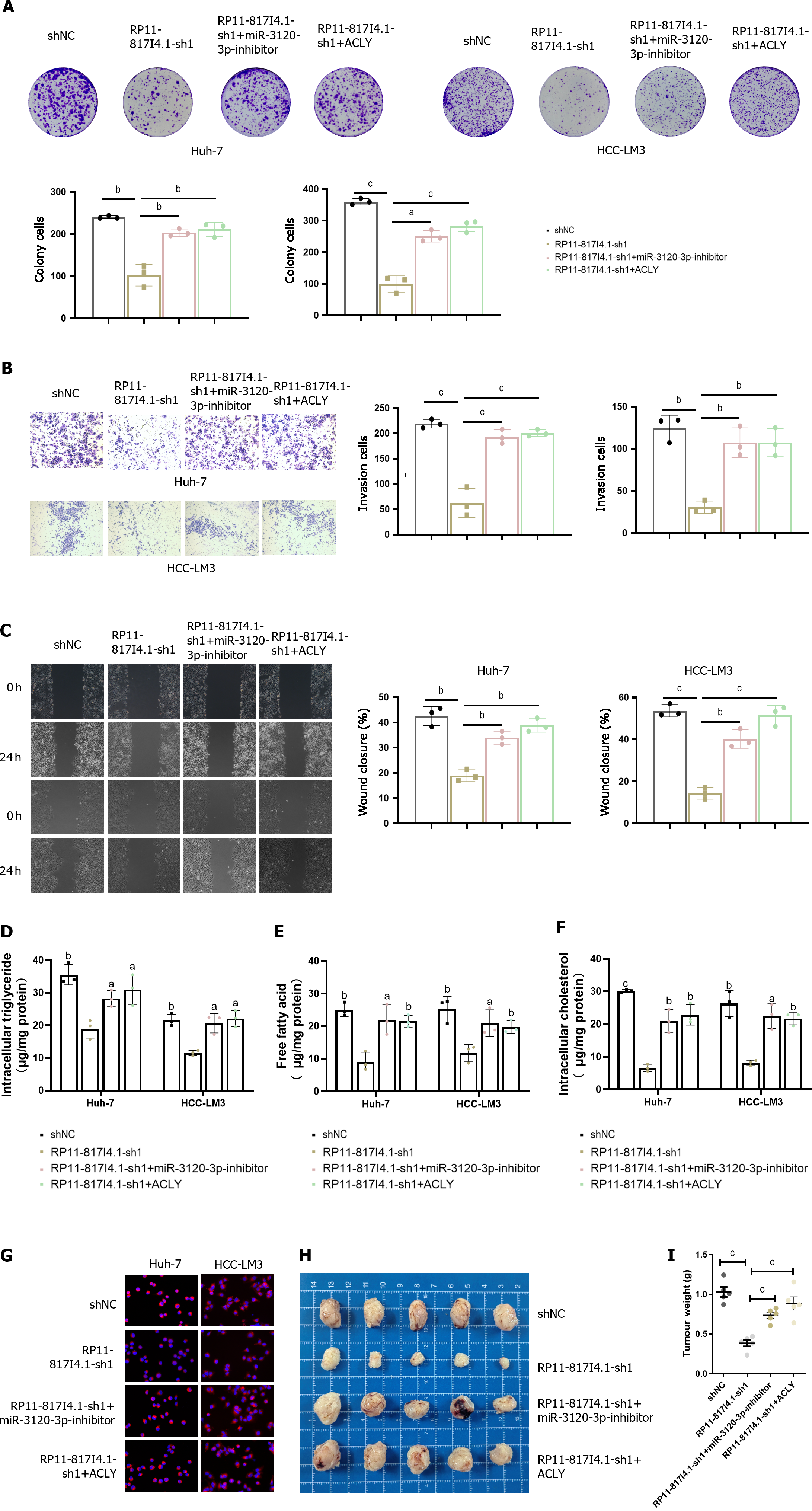
Figure 8 The RP11-817I4.
1/miR-3120-3p/ATP citrate lyase axis promotes lipid synthesis and tumor progression in HCC. A: Colony formation experiment showing the effect of miR-3120-3p and ATP citrate lyase (ACLY) on the change in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) proliferation caused by RP11-817I4.1; B: Transwell experiment showing the effect of miR-3120-3p and ACLY on HCC invasion caused by changes in RP11-817I4.1 cell ability; C: Scratch experiments showing the effect of miR-3120-3p and ACLY on the change in HCC cell migration caused by RP11-817I4.1; D-F: The effects of miR-3120-3p and ACLY on the changes in triglyceride; free fatty acid and cholesterol; levels in HCC cells caused by RP11-817I4.1; G: Nile red staining showing the effects of miR-3120-3p and ACLY on the changes in neutral lipid levels in HCC caused by RP11-817I4.1; H: The subcutaneous tumor model shows the effects of miR-3120-3p and ACLY on the changes in HCC growth caused by RP11-817I4.1 in vivo; I: Weight detection of HCC cells in the subcutaneous tumorigenesis model. The data are presented as the mean ± SD and are representative of three independent experiments. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. ACLY: ATP citrate lyase; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Citation: Wang RY, Yang JL, Xu N, Xu J, Yang SH, Liang DM, Li JZ, Zhu H. Lipid metabolism-related long noncoding RNA RP11-817I4.1 promotes fatty acid synthesis and tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(8): 919-942
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i8/919.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i8.919