Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2024; 30(8): 881-900
Published online Feb 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i8.881
Published online Feb 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i8.881
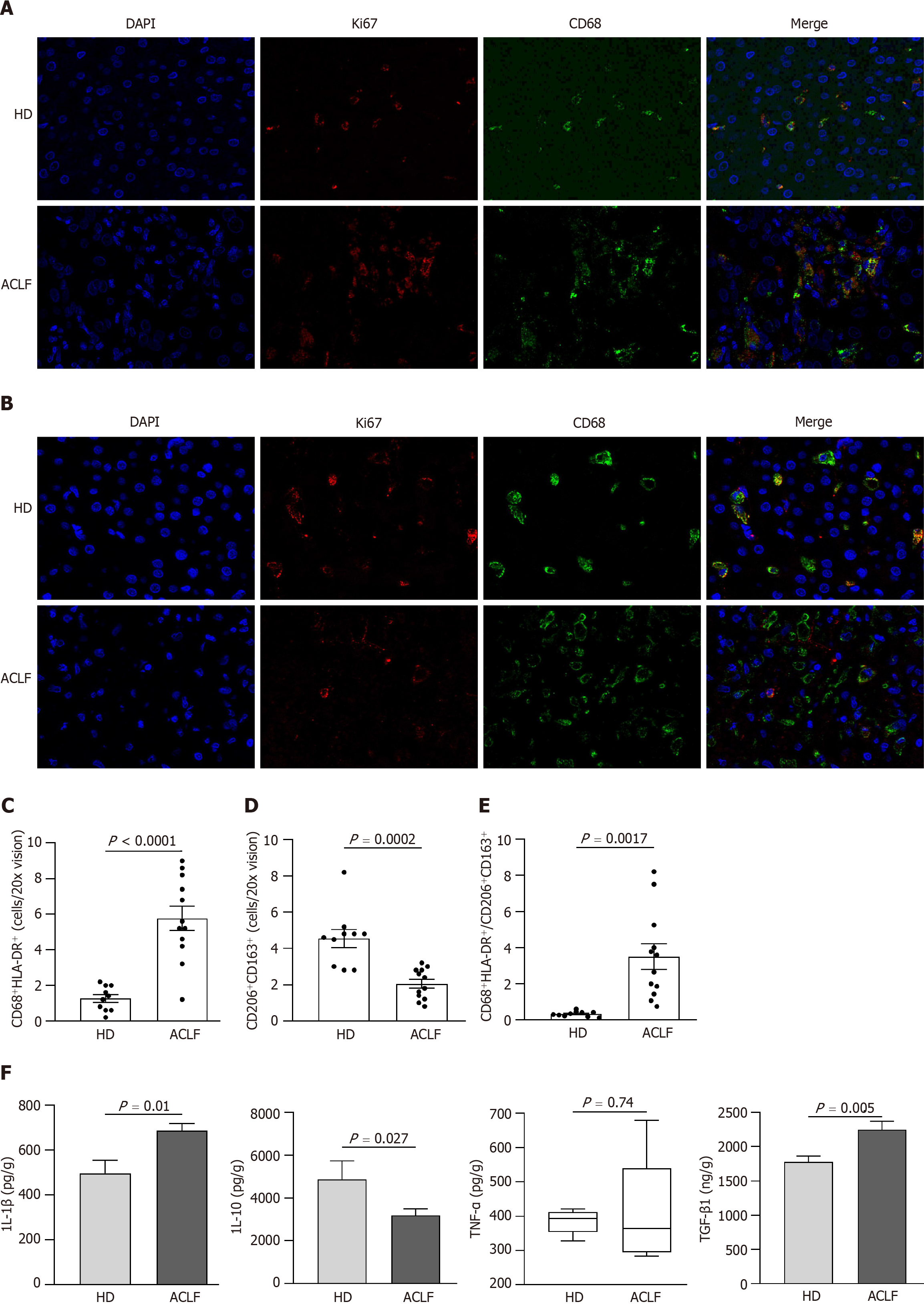
Figure 6 Generalized macrophages activation showed a classically activated phenotype in the liver of patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure.
A: Representative microscopic images of double immunofluorescence staining of CD68 and HLA-DR in the liver (400 fold). The red fluorescence signal represented CD68; the green fluorescence signal represented HLA-DR; and the blue fluorescence signal represented DAPI; B: Representative microscopic images of the double immunofluorescence staining of CD206 and CD163 in the liver (400 fold). The red fluorescence signal represented CD206; the green fluorescence signal represented CD163; and the blue fluorescence signal represented DAPI; C: The mean number of CD68+ HLA-DR+-positive cells in five × 200 fields; D: The mean number of CD206+ CD163+-positive cells in five × 200 fields; E: The ratio of CD68+ HLA-DR+/CD206+ CD163+-positive cells in healthy donors and patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure; F: The levels of macrophage-derived cytokines (interleukin-1β, tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-10, and transforming growth factor-β1) in liver homogenates. Data with normal distribution were compared using unpaired student’s t-test, and the Mann-Whitney test was used for non-normal data. ACLF: Acute-on-chronic liver failure; HD: Healthy donor; IL-1β: Interleukin-1β; IL-10: Interleukin-10; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; TGF-β1: Transforming growth factor.
- Citation: Zhang Y, Tian XL, Li JQ, Wu DS, Li Q, Chen B. Mitochondrial dysfunction affects hepatic immune and metabolic remodeling in patients with hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(8): 881-900
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i8/881.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i8.881