Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2024; 30(8): 833-842
Published online Feb 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i8.833
Published online Feb 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i8.833
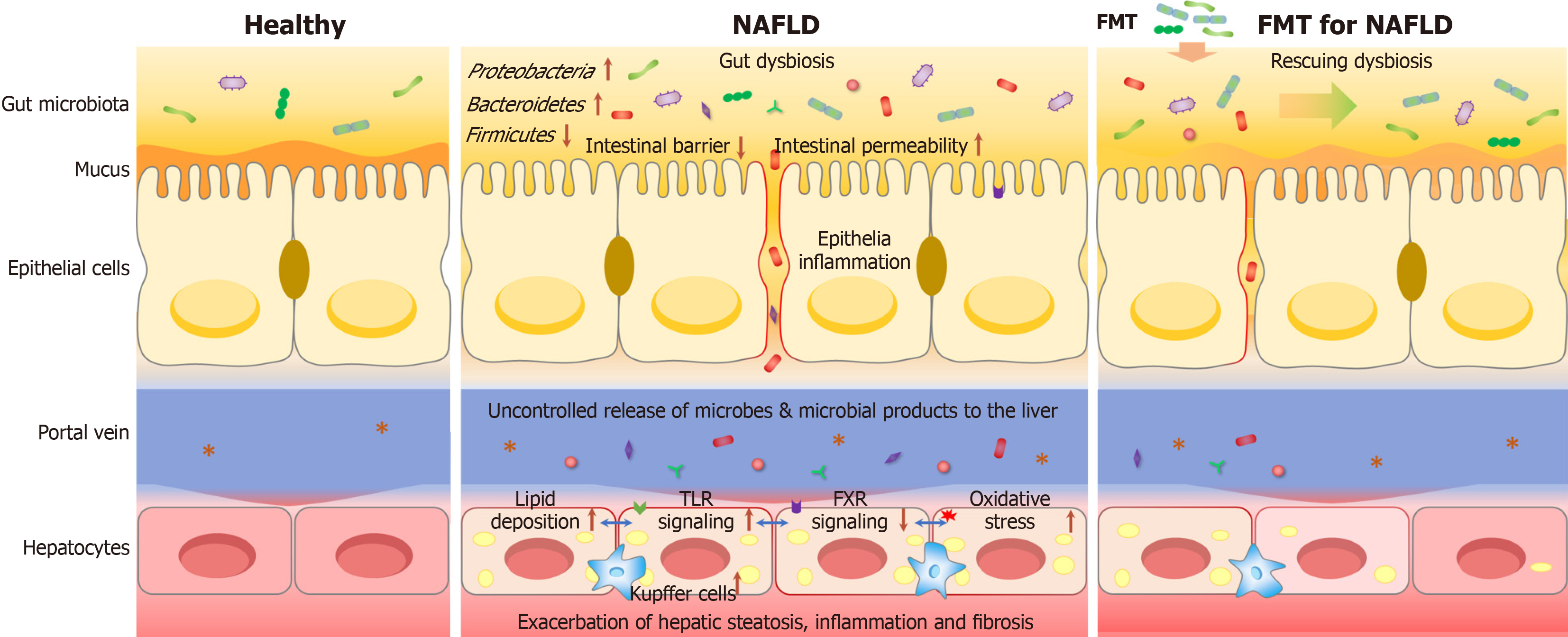
Figure 1 Homeostatic and disrupted gut-liver crosstalk, and mechanism of fecal microbiota transplantation for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease treatment.
Left: Healthy/homeostatic condition; Middle: In non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), the intestinal barrier can be disrupted, which facilitates the translocation of microbes and microbial metabolites to the liver, thus promoting hepatic steatosis, inflammation and fibrosis; Right: Fecal microbiota transplantation is used to recover microbial diversity and abundance and restore homeostatic gut-liver crosstalk, and consequently attenuate the symptoms of NAFLD; FMT: Fecal microbiota transplantation.
- Citation: Qiu XX, Cheng SL, Liu YH, Li Y, Zhang R, Li NN, Li Z. Fecal microbiota transplantation for treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Mechanism, clinical evidence, and prospect. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(8): 833-842
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i8/833.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i8.833