Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2024; 30(7): 728-741
Published online Feb 21, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i7.728
Published online Feb 21, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i7.728
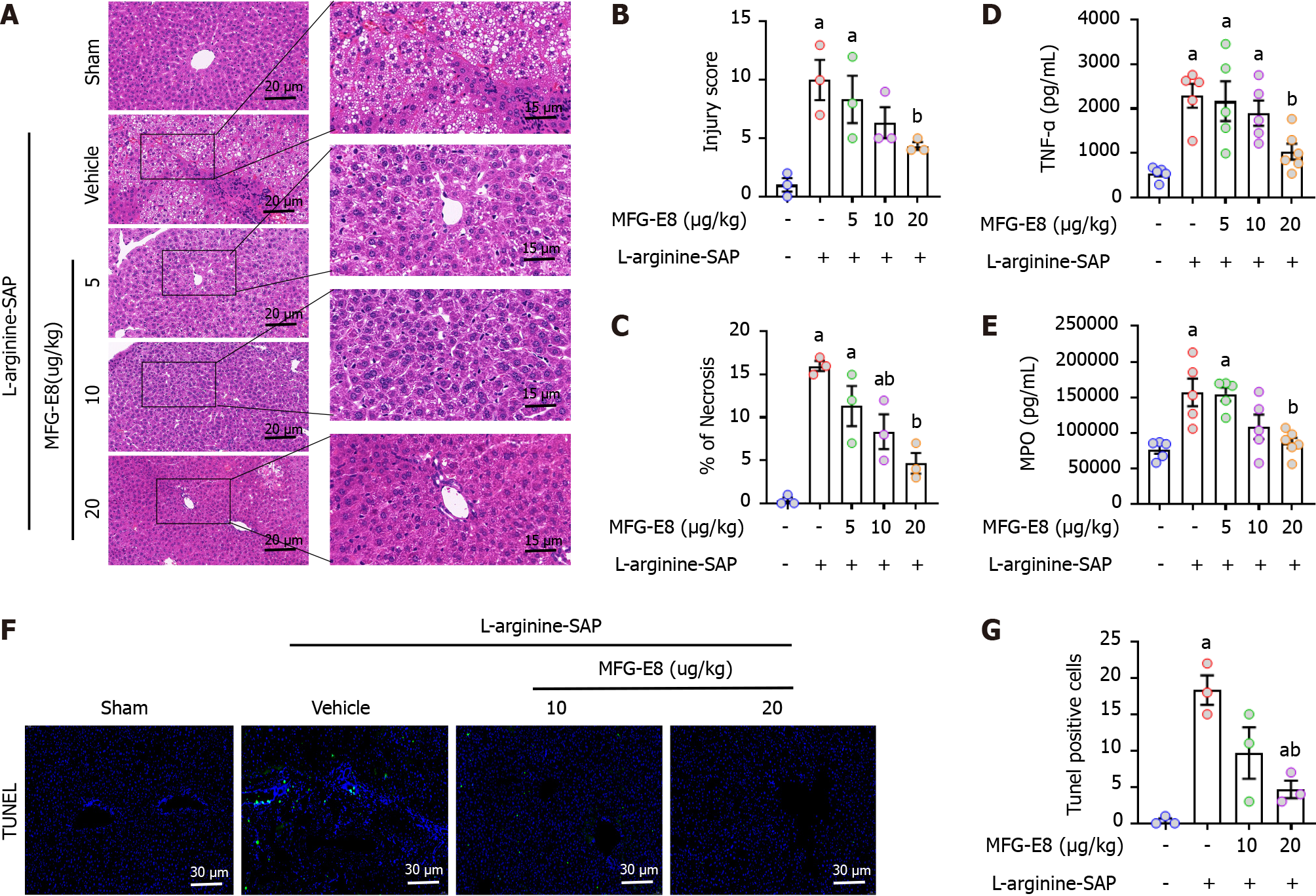
Figure 4 Milk fat globule epidermal growth factor 8 administration mitigates liver Injury in experimental severe acute pancreatitis.
In mice, severe acute pancreatitis was induced by 2 hly intraperitoneal injections of 4.0 g/kg L-arginine. At 2 h after the last injection of L-arginine, normal saline (vehicle) or 5, 10, or 20 μg/kg milk fat globule epidermal growth factor 8 (MFG-E8) was administered through intraperitoneal injection. The animals were sacrificed at 69 h after MFG-E8 treatment (i.e., 72 h after the first injection of L-arginine). Blood and tissue samples were collected. A: Representative photos of hematoxylin and eosin staining in the liver (400 × or 1000 ×); B: Hepatic injury scores; C: Percentages of necrotic areas; D: Tumor necrosis factor-α levels in the liver; E: Myeloperoxidase levels in the liver; F and G: Representative photos of TdT-mediated dUTP Nick-End Labeling (TUNEL) staining (400 ×) and quantitative of TUNEL staining. n = 3-6/group, error bars indicate the SEM; aP < 0.05 vs sham group; bP < 0.05 vs vehicle group. SAP: Severe acute pancreatitis; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; MPO: Myeloperoxidase; TUNEL: TdT-mediated dUTP Nick-End Labeling; MFG-E8: Milk fat globule epidermal growth factor 8.
- Citation: Cui Q, Liu HC, Liu WM, Ma F, Lv Y, Ma JC, Wu RQ, Ren YF. Milk fat globule epidermal growth factor 8 alleviates liver injury in severe acute pancreatitis by restoring autophagy flux and inhibiting ferroptosis in hepatocytes. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(7): 728-741
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i7/728.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i7.728