Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2024; 30(7): 714-727
Published online Feb 21, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i7.714
Published online Feb 21, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i7.714
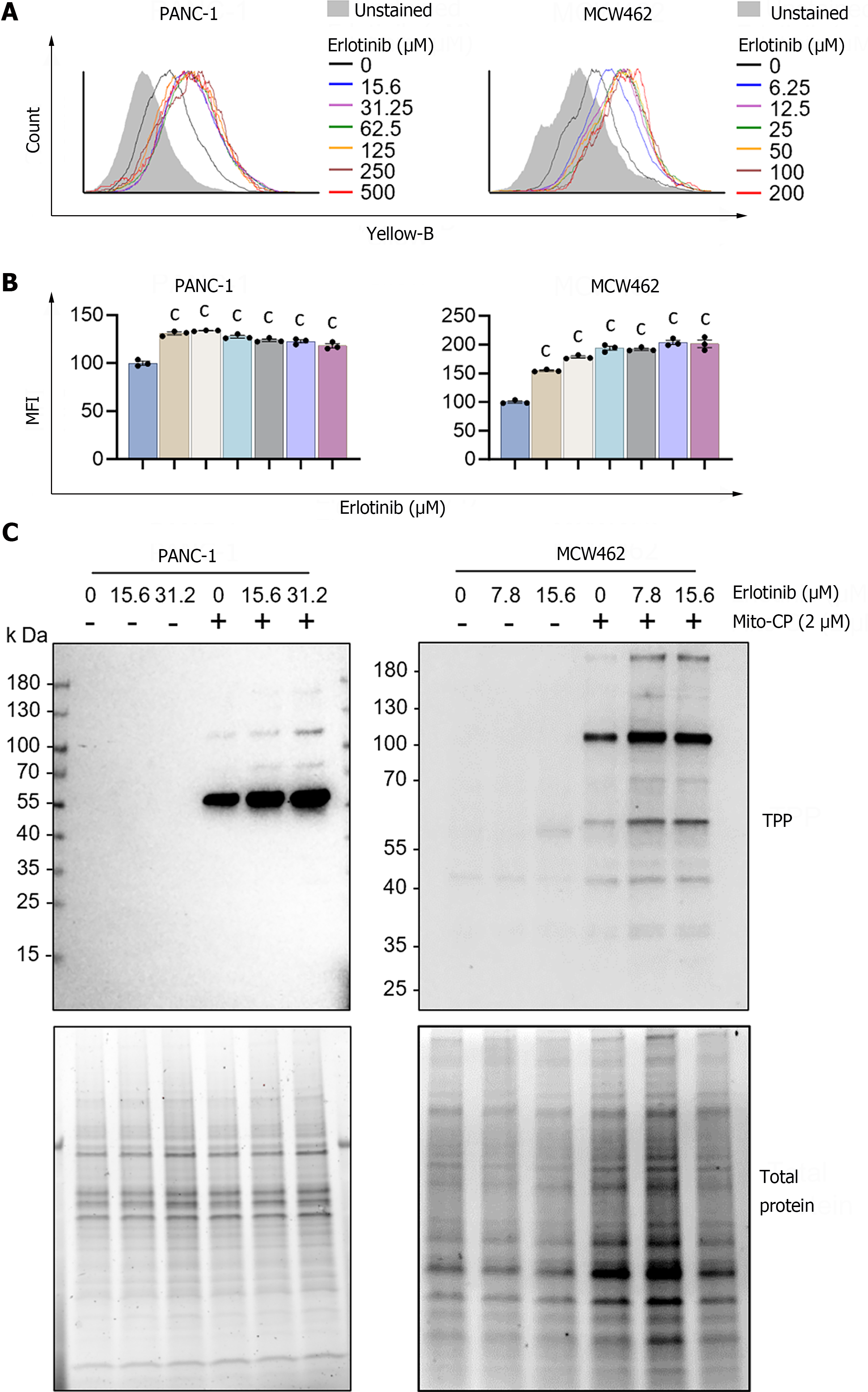
Figure 3 Erlotinib can increase mitochondrial membrane potential in pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells.
A: Cells were treated with increasing concentrations of erlotinib for 2 d prior to staining with tetramethyl-rhodamine methyl ester (TMRM). Cellular TMRM retention was analyzed by flow cytometry measuring yellow fluorescence; B: Mean fluorescence intensities of TMRM-stained cells quantified by FCS Express software. Data are mean ± SEM (n ≥ 3). One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-tests; C: Cells pretreated with erlotinib for 48 h were treated with 2 μM mitochondria-targeted carboxy-proxyl (MitoCP) for 1 h. Mitochondrial extracts of these cells were analyzed by Western blotting to detect the formation of MitoCP adducts using the antibody specific to the triphenyl-phosphonium moiety of MitoCP. Total proteins in the extracts were visualized in the stain-free gel as the control for equal protein loading. cP < 0.001. MitoCP: Mitochondria-targeted carboxy-proxyl; TPP: Triphenyl-phosphonium.
- Citation: Leung PY, Chen W, Sari AN, Sitaram P, Wu PK, Tsai S, Park JI. Erlotinib combination with a mitochondria-targeted ubiquinone effectively suppresses pancreatic cancer cell survival. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(7): 714-727
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i7/714.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i7.714