Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2024; 30(7): 714-727
Published online Feb 21, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i7.714
Published online Feb 21, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i7.714
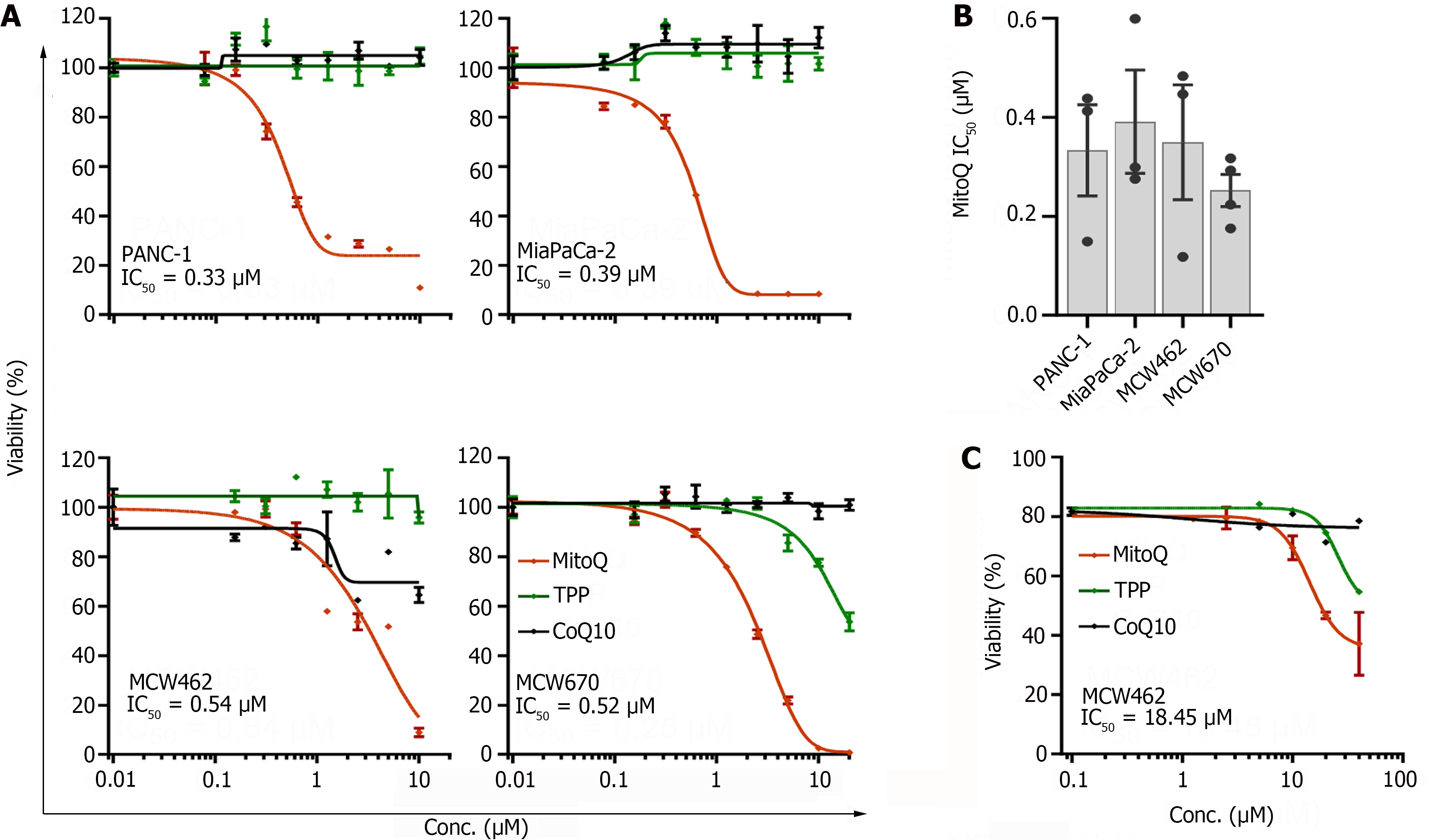
Figure 1 Mitochondria-targeted ubiquinone can suppress the viability of pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells.
A: pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cells in 12 well plates were treated with increasing doses of mitochondria-targeted ubiquinone (MitoQ), CoQ10, and triphenyl-phosphonium (TPP) for 48 h prior to determining cell viability by crystal violet staining. CoQ10 is the functional moiety of MitoQ and TPP is the vehicle moiety. 462 and 670 denote MCW462 and MCW670 cell lines, respectively; B Summary of the half maximal inhibitory concentration values determined for different PDAC cells treated and analyzed as described; C: MCW462 cells in organoid cultures were treated with increasing doses of MitoQ, CoQ10, and TPP for 48 h prior to determining cell viability by Sytox Green assays. Data (mean ± SEM, n ≥ 3) are expressed as the percentage of untreated controls. TPP: Triphenyl-phosphonium; MitoQ: Mitochondria-targeted ubiquinone; IC50: Half maximal inhibitory concentration.
- Citation: Leung PY, Chen W, Sari AN, Sitaram P, Wu PK, Tsai S, Park JI. Erlotinib combination with a mitochondria-targeted ubiquinone effectively suppresses pancreatic cancer cell survival. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(7): 714-727
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i7/714.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i7.714