Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2024; 30(7): 685-704
Published online Feb 21, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i7.685
Published online Feb 21, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i7.685
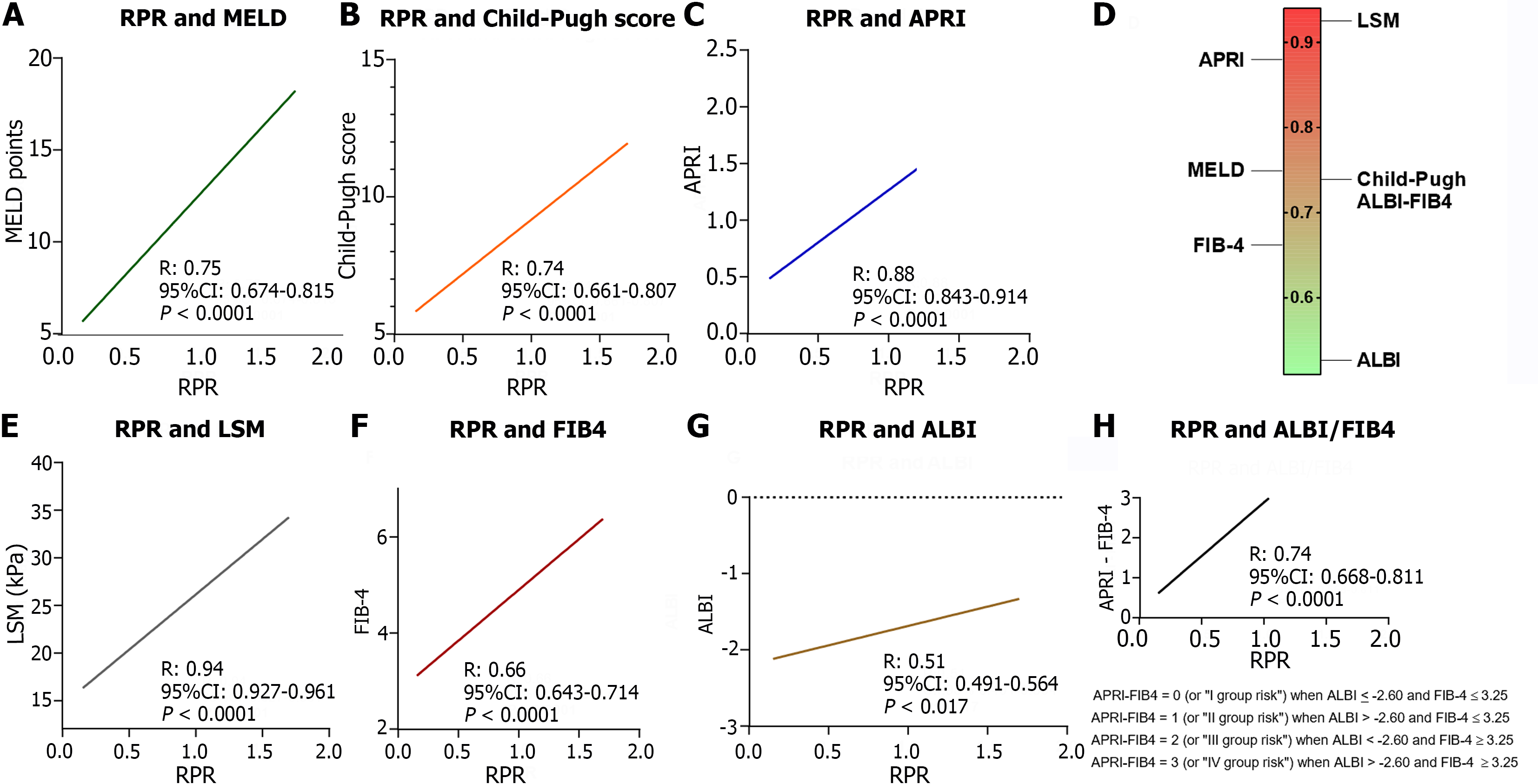
Figure 3 Relationship between baseline red cell distribution width/platelet ratio values and validated tools non-invasively assessing liver-function status and hepatic fibrosis.
A, B, C, E, F, G and H: Linear regression of red cell distribution width to platelet ratio (RPR) and Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (A); RPR and Child-Push score (B); RPR and aspartate aminotransferase/platelet count ratio index (C); RPR and Liver Stiffness Measurement (E); RPR and Fibrosis-4 (FIB-4; F); RPR and Albumin-Bilirubin (ALBI; G); RPR and ALBI/FIB-4 (H). D: Heat map of R values revealed of to the linear regression analysis between baseline RPR others tools reported in panel A, B, C, E, F, G, H. LSM: Liver Stiffness Measurement; ALBI: Albumin-Bilirubin; FIB-4: Fibrosis-4; APRI: Aspartate aminotransferase/platelet count ratio index; MELD: Model for End-Stage Liver Disease; RPR: Red cell distribution width to platelet ratio.
- Citation: Dallio M, Romeo M, Vaia P, Auletta S, Mammone S, Cipullo M, Sapio L, Ragone A, Niosi M, Naviglio S, Federico A. Red cell distribution width/platelet ratio estimates the 3-year risk of decompensation in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease-induced cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(7): 685-704
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i7/685.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i7.685