Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2024; 30(6): 542-555
Published online Feb 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i6.542
Published online Feb 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i6.542
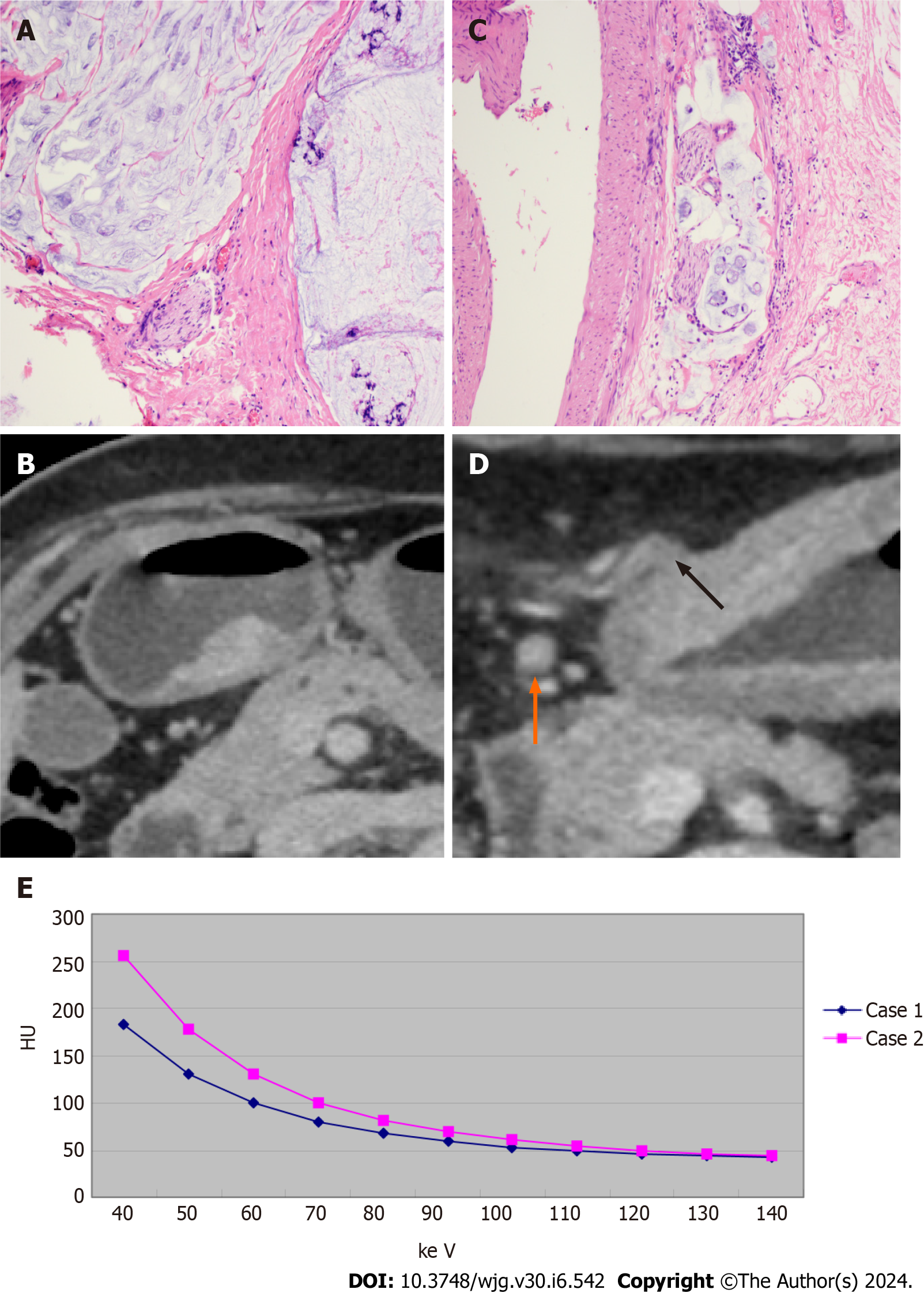
Figure 5 Comparative imaging and spectral analysis of pathological gastric adenocarcinoma in two patients with different lympho
- Citation: Ge HT, Chen JW, Wang LL, Zou TX, Zheng B, Liu YF, Xue YJ, Lin WW. Preoperative prediction of lymphovascular and perineural invasion in gastric cancer using spectral computed tomography imaging and machine learning. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(6): 542-555
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i6/542.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i6.542