Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2024; 30(5): 485-498
Published online Feb 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i5.485
Published online Feb 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i5.485
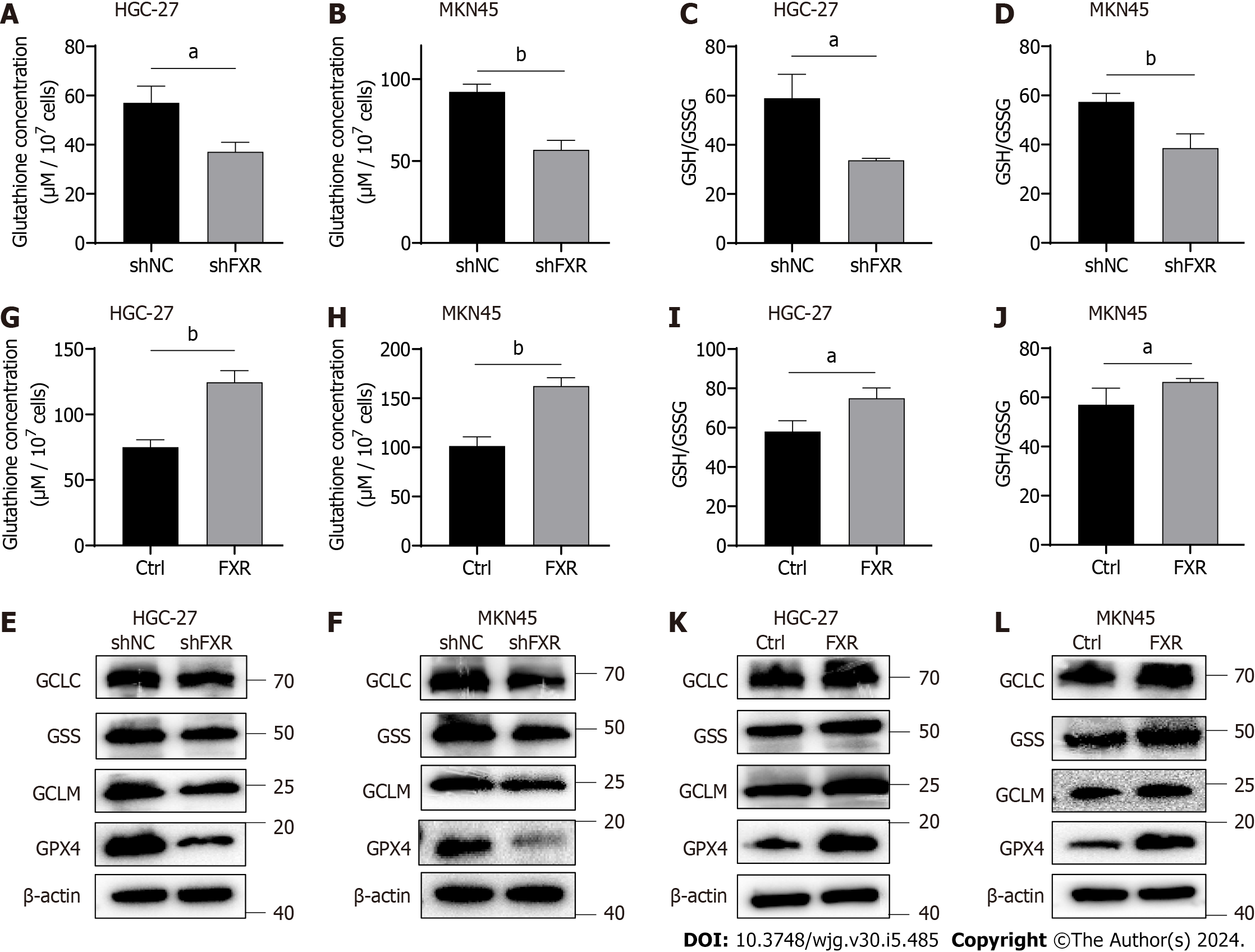
Figure 4 Farnesoid X receptor significantly promoted the synthesis of glutathione and the level of glutathione peroxidase 4 in gastric cancer cells.
A-D: Alterations of glutathione (GSH) concentrations and the GSH/oxidized GSH (GSSG) ratio in HGC-27 and MKN-45 cells transfected with the shNC or shFXR plasmid; E and F: Protein expression of GCLC, GSS, GCLM, and GSH peroxidase 4 (GPX4) in HGC-27 and MKN-45 cells transfected with the shNC or shFXR plasmid; G-J: Alterations of GSH concentrations and the GSH/GSSG ratio in HGC-27 and MKN-45 cells transfected with the control or farnesoid X receptor (FXR)-coding plasmid; K and L: Protein expression of GCLC, GSS, GCLM, and GPX4 in HGC-27 and MKN-45 cells transfected with the control or FXR-coding plasmid. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. These experiments were repeated three times. FXR: Farnesoid X receptor; GPX4: Glutathione peroxidase 4.
- Citation: Liu CX, Gao Y, Xu XF, Jin X, Zhang Y, Xu Q, Ding HX, Li BJ, Du FK, Li LC, Zhong MW, Zhu JK, Zhang GY. Bile acids inhibit ferroptosis sensitivity through activating farnesoid X receptor in gastric cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(5): 485-498
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i5/485.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i5.485