Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2024; 30(5): 485-498
Published online Feb 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i5.485
Published online Feb 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i5.485
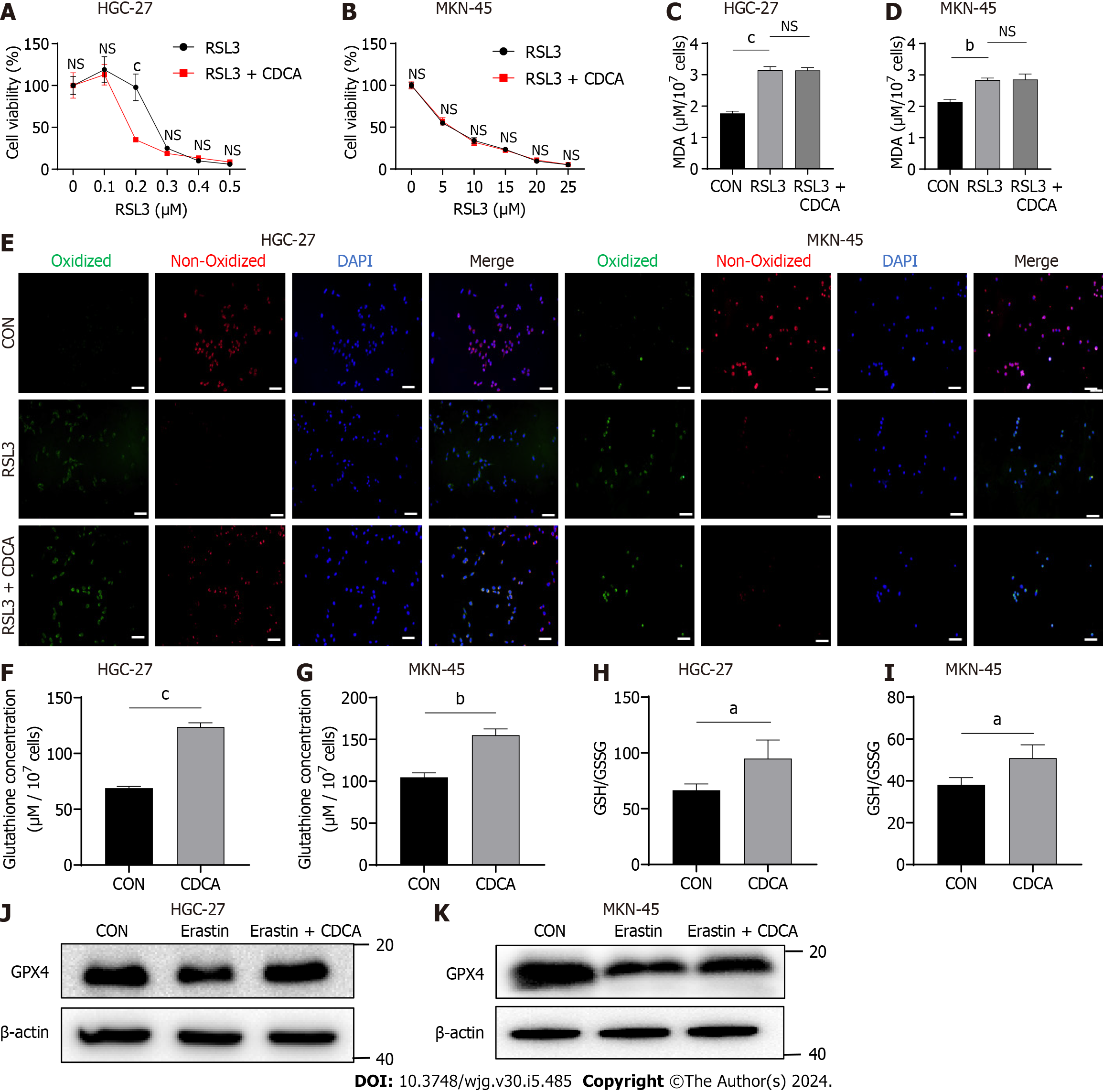
Figure 2 Bile acids significantly upregulated glutathione and glutathione peroxidase 4 in gastric cancer cells.
A and B: Cell viability assay of two gastric cancer cell lines treated with RSL3 together with chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) or control; C and D: Malondialdehyde production in HGC-27 and MKN-45 cells treated with RSL3 (0.2 μM for HGC-27, 10 μM for MKN-45) followed by CDCA or control; E: BODIPY-589/591 C11 staining to identify lipid reactive oxygen species in the cell lines treated with RSL3 (0.2 μM for HGC-27, 10 μM for MKN-45) followed by CDCA or control; F and G: The glutathione (GSH) concentrations were measured in cells treated with CDCA; H and I: The GSH/oxidized GSH ratio was measured in cells treated with CDCA; J and K: Western blot analysis of GSH peroxidase 4 protein expression in HGC-27 and MKN-45 cells under different stimuli. Scale bar: 100 μm. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. These experiments were repeated three times. CDCA: Chenodeoxycholic acid; MDA: Malondialdehyde; GPX4: Glutathione peroxidase 4; NS: Not significant.
- Citation: Liu CX, Gao Y, Xu XF, Jin X, Zhang Y, Xu Q, Ding HX, Li BJ, Du FK, Li LC, Zhong MW, Zhu JK, Zhang GY. Bile acids inhibit ferroptosis sensitivity through activating farnesoid X receptor in gastric cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(5): 485-498
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i5/485.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i5.485