Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2024; 30(5): 471-484
Published online Feb 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i5.471
Published online Feb 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i5.471
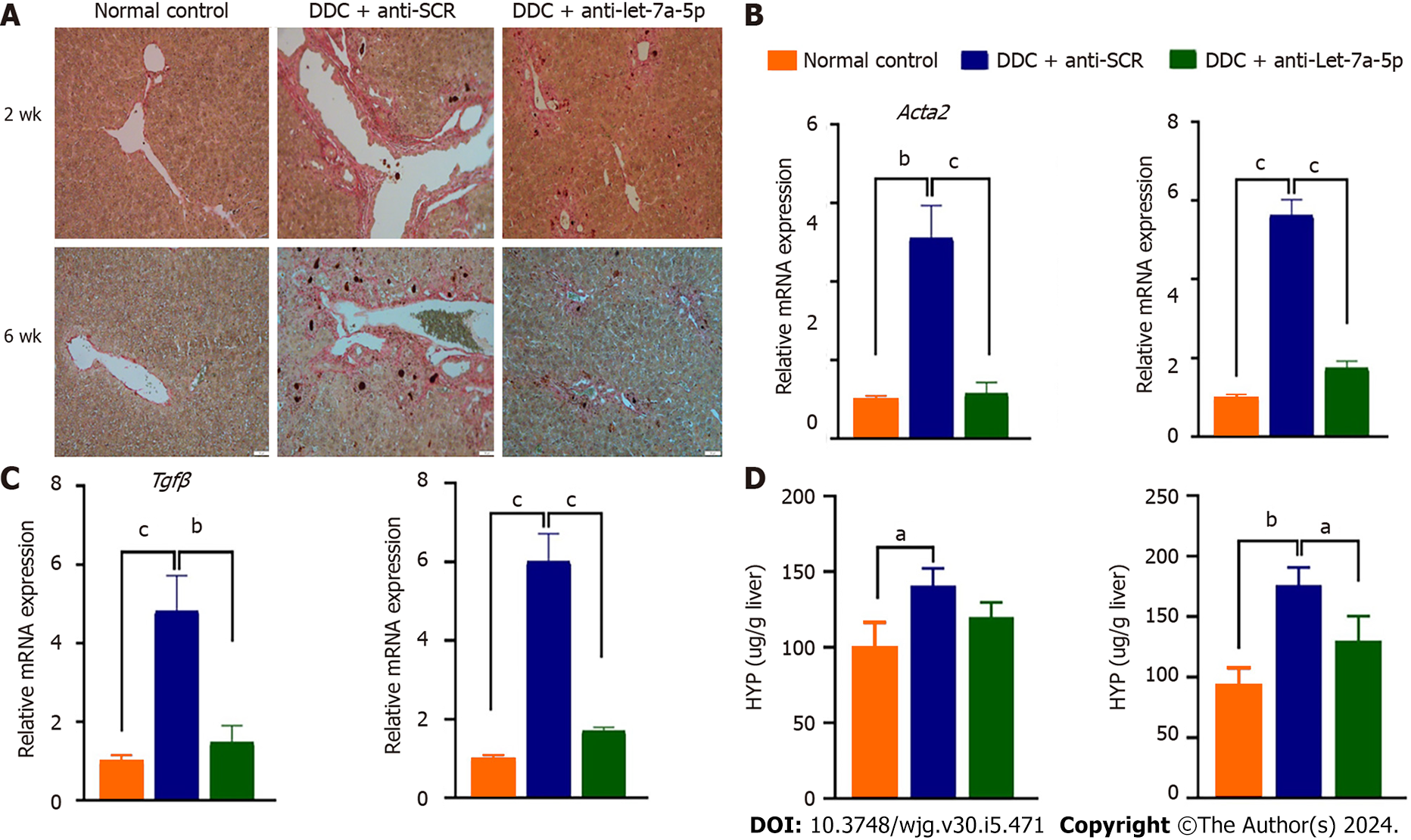
Figure 5 Let-7a-5p inhibition mediated by recombinant adeno-associated virus 8 ameliorates biliary fibrosis in the 3,5-Diethoxycarbonyl-1,4-Dihydrocollidine-induced cholestasis model.
A: Sirius Red staining in the liver of mice at 2 wk and 6 wk after 3,5-Diethoxycarbonyl-1,4-Dihydrocollidine feeding; B and C: The fibrosis markers such as Acta 2 and Tgfb were evaluated using qRT-PCR; D: The contents of Hyp in the liver of mice in each group were determined. DDC: 3,5-Diethoxycarbonyl-1,4-Dihydrocollidine; SCR: Scramble control; Hyp: Hydroxyproline. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001.
- Citation: Hua H, Zhao QQ, Kalagbor MN, Yu GZ, Liu M, Bian ZR, Zhang BB, Yu Q, Xu YH, Tang RX, Zheng KY, Yan C. Recombinant adeno-associated virus 8-mediated inhibition of microRNA let-7a ameliorates sclerosing cholangitis in a clinically relevant mouse model. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(5): 471-484
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i5/471.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i5.471