Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2024; 30(47): 4991-5006
Published online Dec 21, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i47.4991
Published online Dec 21, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i47.4991
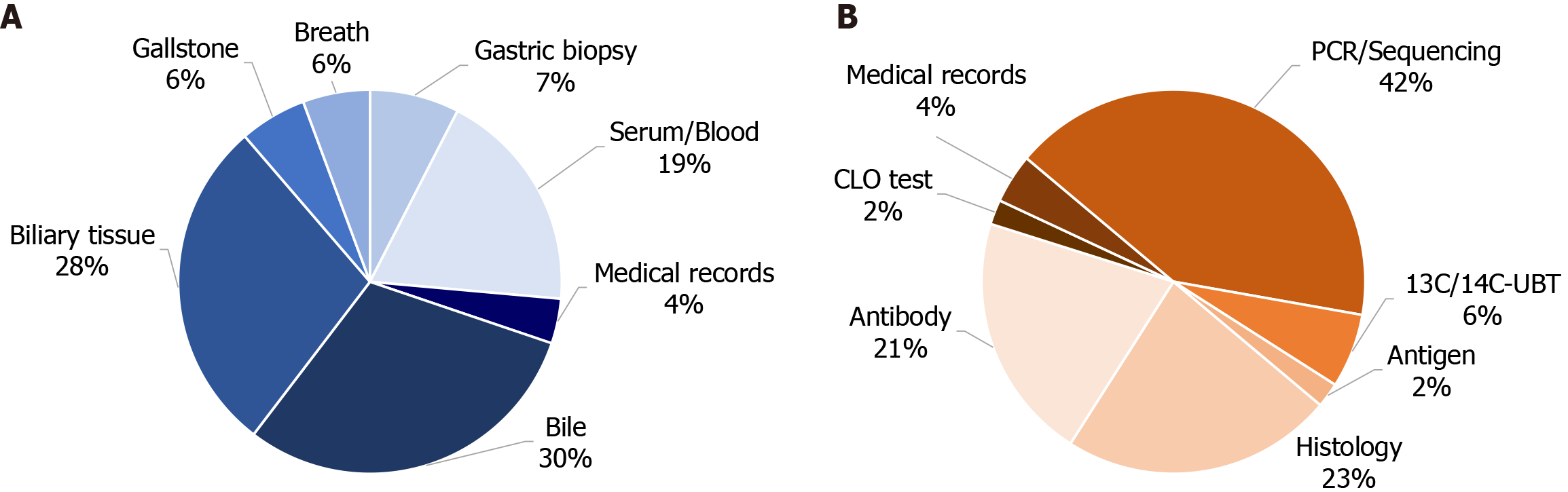
Figure 3 The distribution of sample sources and detection methods for Helicobacter pylori of included studies.
A: Sample sources for Helicobacter pylori; B: Detection methods for Helicobacter pylori. Detailed data shown in Table 4. 13C/14C-UBT: 13C or 14C urease breath test; CLO: Campylobacter-like organism; PCR: Polymerase chain reaction.
- Citation: Yao SY, Li XM, Cai T, Li Y, Liang LX, Liu XM, Lei YF, Zhu Y, Wang F. Helicobacter pylori infection is associated with the risk and phenotypes of cholelithiasis: A multi-center study and meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(47): 4991-5006
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i47/4991.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i47.4991