Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2024; 30(46): 4937-4946
Published online Dec 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i46.4937
Published online Dec 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i46.4937
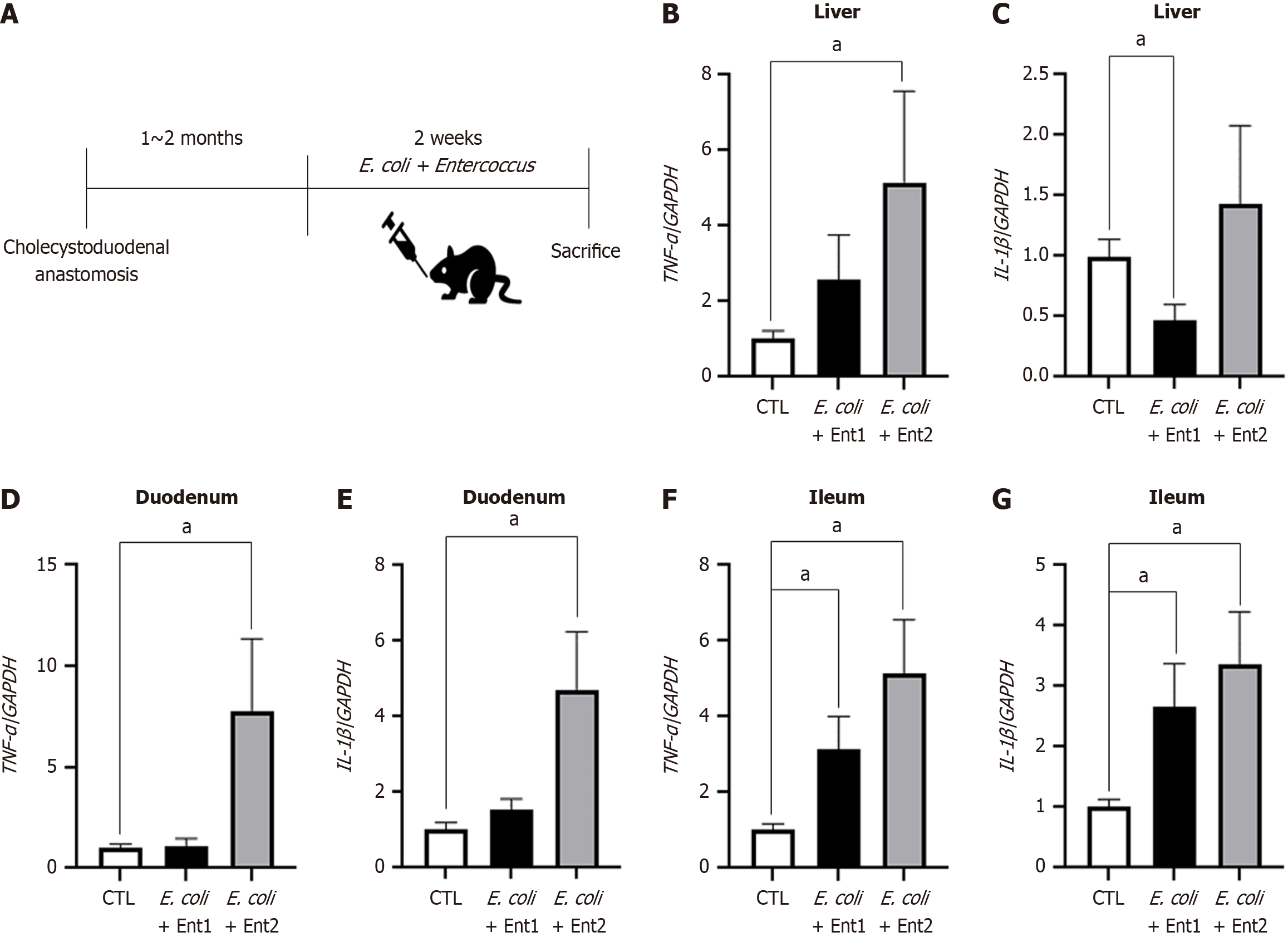
Figure 6 mRNA levels of proinflammatory cytokines in cholecystoduodenal anastomosis and control mice.
Mixture of Escherichia coli and Enterococcus (E. coli + Ent1: 6 × 108 and E. coli + Ent2: 3 × 109) was orally administered to cholecystoduodenal anastomosis mice for 2 weeks. A: Injection schedule of bacteria; B-G: TNF-α and IL-1β mRNA levels in the liver, duodenum, and ileum of each group after injection of saline or harmful bacteria. Values are normalized to GAPDH levels and represented as the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05 vs corresponding controls. E. coli: Escherichia coli; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; IL: Interleukin.
- Citation: Jang Y, Kim JY, Han SY, Park A, Baek SJ, Lee G, Kang J, Ryu H, Kim SH. Establishment of a chronic biliary disease mouse model with cholecystoduodenal anastomosis for intestinal microbiome preservation. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(46): 4937-4946
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i46/4937.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i46.4937