Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2024; 30(46): 4937-4946
Published online Dec 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i46.4937
Published online Dec 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i46.4937
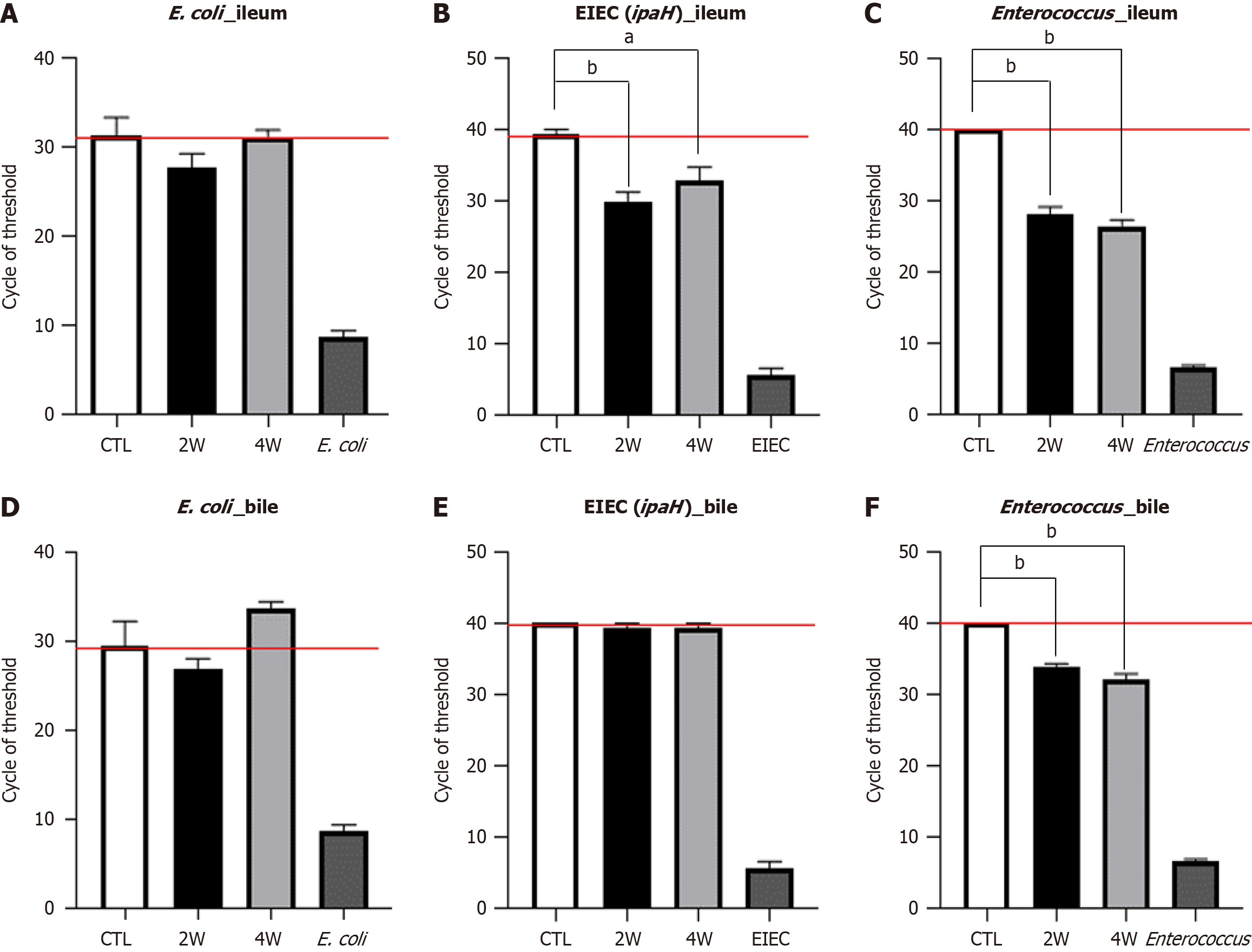
Figure 5 Quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction analysis of 16s rRNA and ipaH genes in the ileum and bile of cholecystoduodenal anastomosis mice after injection of bacteria.
A: The mixture of Escherichia coli and Enterococcus was orally administered to cholecystoduodenal anastomosis mice. Bacterial gene was detected in the ileum using specific 16s rRNA primers; B-F: Cycle threshold (CT) of bacterial gene expression detected in the ileum and bile using EIEC-specific ipaH gene primers and 16s rRNA primers. Values are normalized to GAPDH levels and are represented as the mean ± SD. aP < 0.01, bP < 0.001 vs corresponding controls. 2W: 2 weeks after injection; 4W: 4 weeks after injection; CTL: Control; E. coli: Escherichia coli.
- Citation: Jang Y, Kim JY, Han SY, Park A, Baek SJ, Lee G, Kang J, Ryu H, Kim SH. Establishment of a chronic biliary disease mouse model with cholecystoduodenal anastomosis for intestinal microbiome preservation. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(46): 4937-4946
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i46/4937.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i46.4937