Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2024; 30(46): 4864-4879
Published online Dec 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i46.4864
Published online Dec 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i46.4864
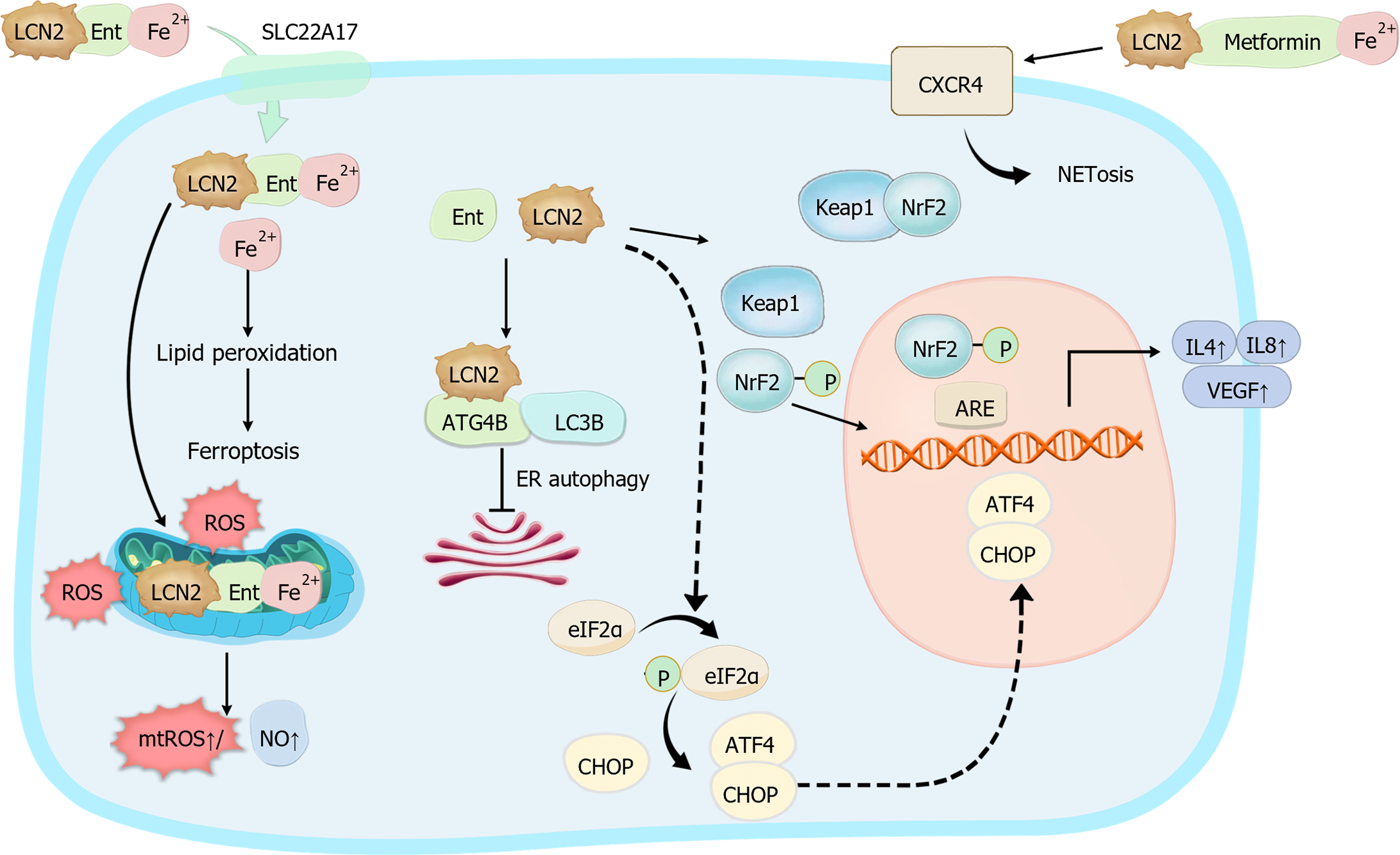
Figure 3 Mechanisms by which lipocalin-2 interacts with cells (schematic diagram).
The mechanisms by which lipocalin-2 complexes exert their effects on cells have been summarized. SLC22A17: Solute carrier family 22 member 17; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; ATG4B: Autophagy-related gene 4B; LC3B: Light-chain 3B; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; elF2α: Alpha-subunit of eukaryotic translational initiation factor 2; ATF4: Activating transcription factor 4; CHOP: C/EBP homologous protein; Keap1: Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; NrF2: Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; VEGF: Vascular endothelial-derived growth factor; CXCR4: C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4; LCN2: Lipocalin-2; ARE: Antioxidant response elements.
- Citation: Zhang ZX, Peng J, Ding WW. Lipocalin-2 and intestinal diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(46): 4864-4879
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i46/4864.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i46.4864