Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2024; 30(45): 4817-4835
Published online Dec 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i45.4817
Published online Dec 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i45.4817
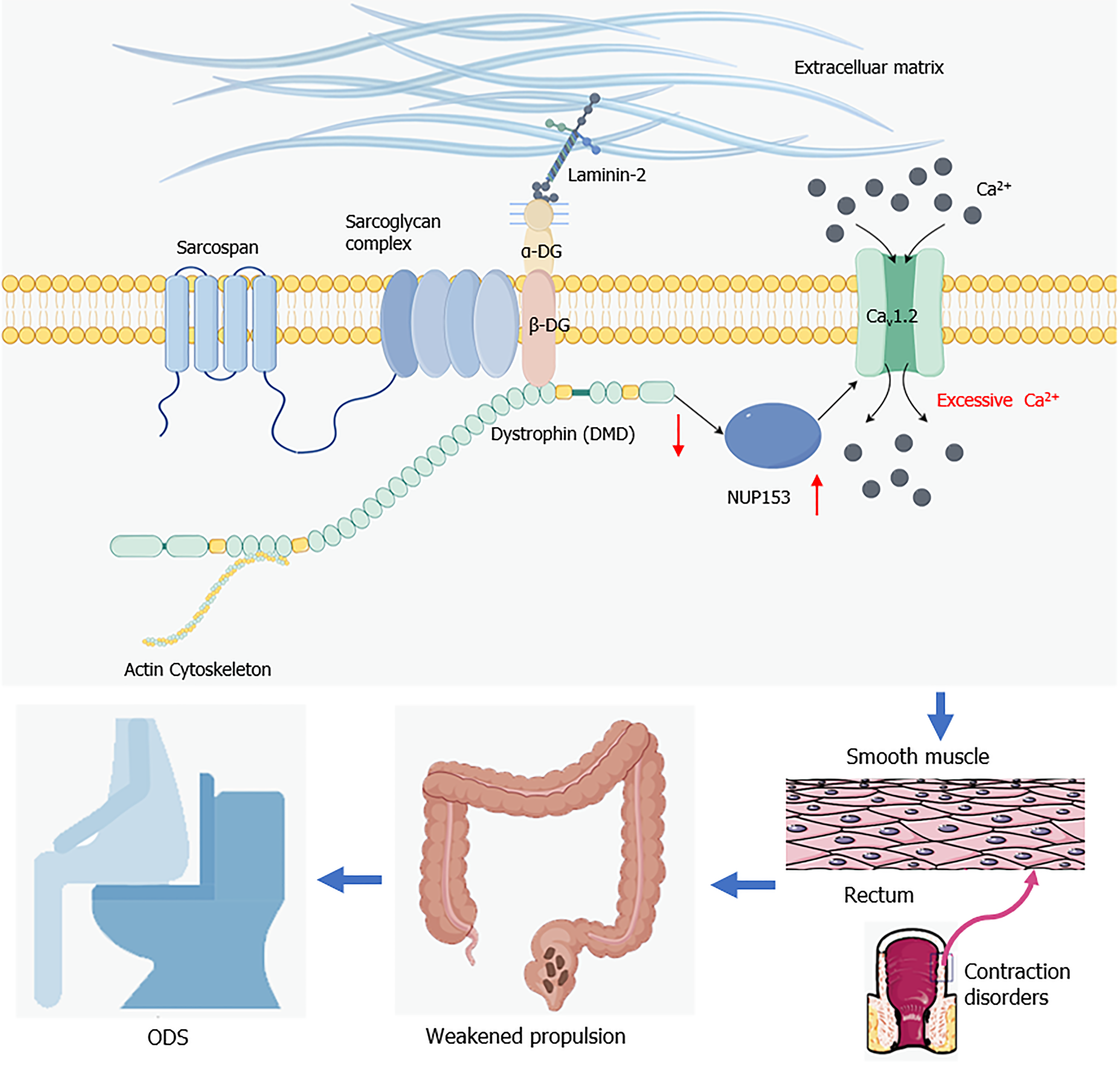
Figure 7 Diagram illustrating role of dystrophin in obstructed defecation syndrome (created with Figdraw 2.
0). In intestinal smooth muscle cells, altered expression of dystrophin affects the expression of nucleoporin protein 153, leading to its L-type voltage-gated calcium channel being overactivated and increasing calcium influx. Under these circumstances, the contractile function of intestinal smooth muscle cells is impaired, resulting in insufficient rectal propulsion force, ultimately leading to obstructed defecation syndrome. ODS: Obstructed defecation syndrome; NUP153: Nucleoporin protein 153; Cav1.2: L-type voltage-gated calcium channel.
- Citation: Li WZ, Xiong Y, Wang TK, Chen YY, Wan SL, Li LY, Xu M, Tong JJ, Qian Q, Jiang CQ, Liu WC. Quantitative proteomics analysis reveals the pathogenesis of obstructed defecation syndrome caused by abnormal expression of dystrophin. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(45): 4817-4835
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i45/4817.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i45.4817