Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2024; 30(45): 4817-4835
Published online Dec 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i45.4817
Published online Dec 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i45.4817
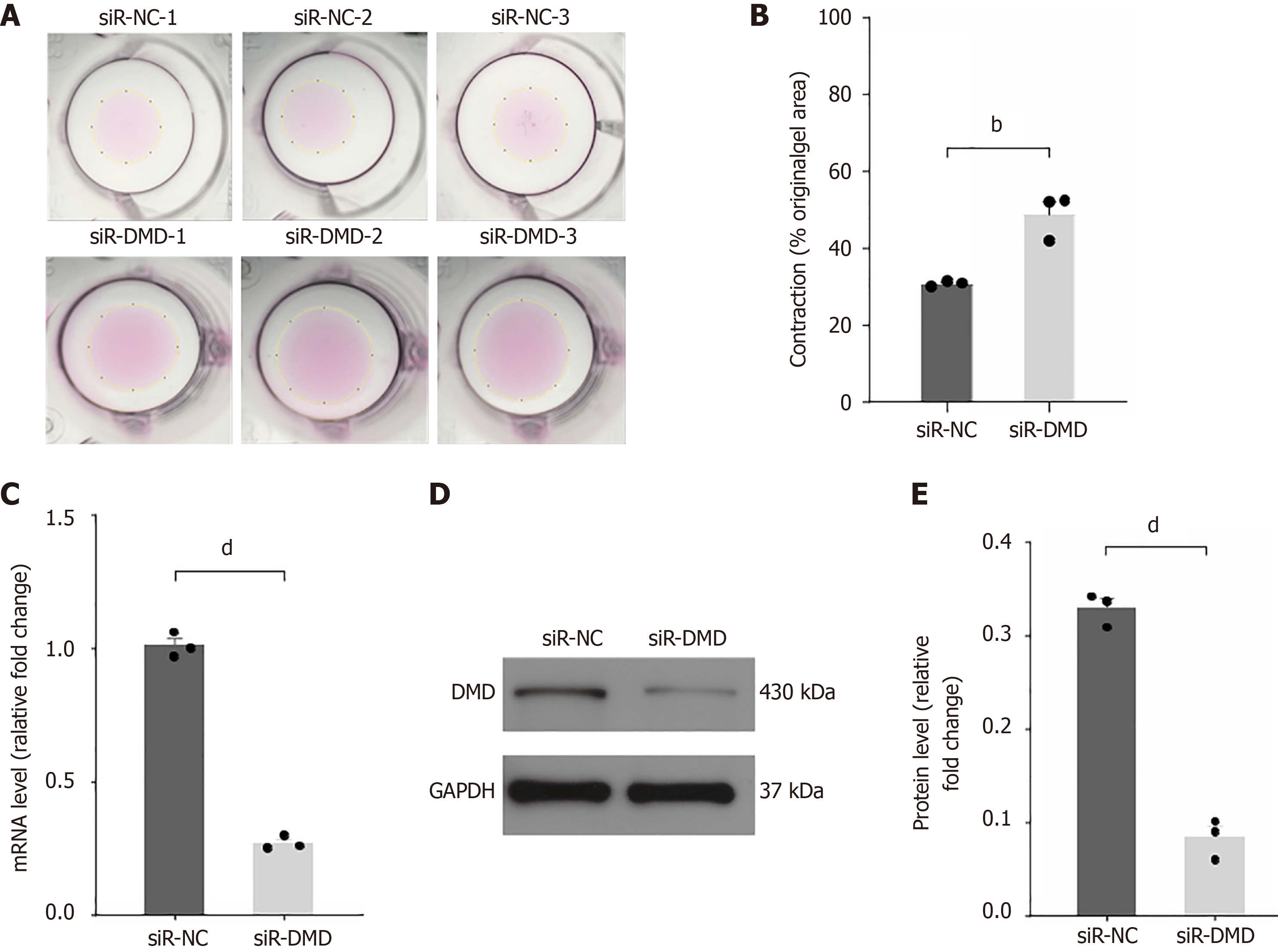
Figure 3 Downregulation of dystrophin expression is associated with impaired contraction of human intestinal smooth muscle cells.
A: Assessment of contractile function in intestinal smooth muscle cells after transfection with negative control small interfering RNA (siR-NC) (top) or siR-dystrophin (siR-DMD) (bottom); B: Quantitative analysis of cell area after contraction in both groups; C: Detection of DMD expression in human intestinal smooth muscle cells transfected with siR-NC or siR-DMD by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction; D: Western blot detection of DMD expression in whole cell extracts of human intestinal smooth muscle cells transfected with siR-NC or siR-DMD; E: Quantitative analysis of Western blot greyscale value. bP < 0.01, dP < 0.0001, n = 3. siR-NC: Negative control small interfering RNA; siR-DMD: Dystrophin small interfering RNA; DMD: Dystrophin.
- Citation: Li WZ, Xiong Y, Wang TK, Chen YY, Wan SL, Li LY, Xu M, Tong JJ, Qian Q, Jiang CQ, Liu WC. Quantitative proteomics analysis reveals the pathogenesis of obstructed defecation syndrome caused by abnormal expression of dystrophin. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(45): 4817-4835
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i45/4817.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i45.4817