Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2024; 30(44): 4768-4770
Published online Nov 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i44.4768
Published online Nov 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i44.4768
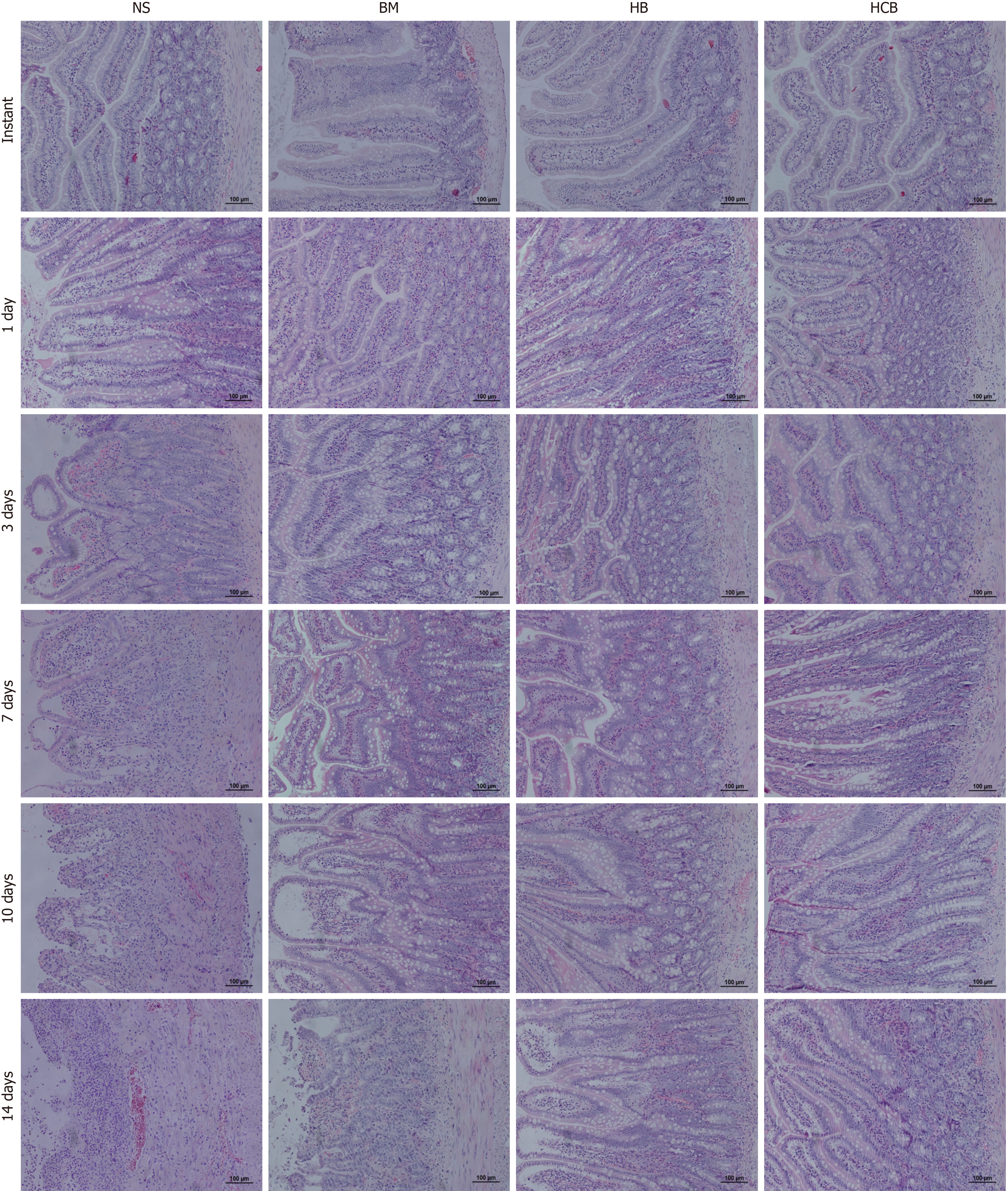
Figure 1 Pathology of transplanted small bowel (Hematoxylin & eosin staining, × 100).
All four groups showed normal histological results immediately after transplant. The normal saline (NS) group showed mild rejection at day 1 after transplantation: Shorter and bifurcated intestinal villi, mild submucosal edema, cryptic epithelial cells with mild damage (cytoplasmic basophilic increase, nuclear enlargement, and color deepening) and increased apoptosis, more than six apoptotic bodies per 10 crypt cells, and mild mononuclear cells which are the main inflammatory cells found during inflammatory infiltration of the lamina propria; in contrast, the bone marrow (BM) group, HO-1-modified BM mesenchymal stem cells (HB) group, and the Adv-(CXCR3 + HO-1)/bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (HCB) group showed only mild edema. The pathological changes at 3 d after transplantation in the NS group were more severe than those at 1 day, where the submucosal edema was aggravated, and there was increased inflammatory infiltration of the lamina propria; the BM group and HB group showed mild inflammatory infiltration of the lamina propria, and the HCB group was similar to the normal intestine. The NS group showed moderate rejection at day 7 after transplantation: A reduced ratio of villous height to crypt, partial necrosis of glandular epithelial cells, aggravated edema and inflammation, diffuse crypt damage and increased apoptosis, and mild arteritis and congestion of lamina propria and submucosa; the BM group and HB group showed mild rejection: The BM group had shorter intestinal villi, mild submucosal edema, inflammatory cell infiltration, mild crypt epithelial injury, and increased apoptosis; the HB group had mild inflammatory cell infiltration, mild crypt injury, with other signs not being obvious; the HCB group were indeterminate for rejection: Mild cryptic epithelial damage and the number of apoptotic bodies increased, with mild, local inflammatory cell infiltration of the lamina propria. The NS group showed severe rejection at day 10 after transplantation: Intestinal villus changes were further aggravated, with serious shedding of the intestinal mucosal epithelial cells, while crypt epithelial injury was very serious; inflammatory cell infiltration involved the muscle layer, resulting in severe arteritis; the pathological changes in the BM group, HB group, and HCB group at day 10 were more severe than those at day 7 after transplantation. The structures of the intestinal mucosa layer were completely destroyed and the intestinal wall became thinner with necrosis in the NS group 14 days after transplantation; the BM group showed moderate rejection; the HB group did not achieve moderate rejection but rejection was more severe than mild; the HCB group showed mild rejection. NS: Normal saline group; BM: Bone marrow; HB: HO-1-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells group; HCB: The Adv-(CXCR3 + HO-1)/bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells group.
- Citation: Yin ML, Song HL, Yang Y, Zheng WP, Liu T, Shen ZY. Correction to: Effect of CXCR3/HO-1 genes modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on small bowel transplant rejection. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(44): 4768-4770
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i44/4768.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i44.4768