Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2024; 30(41): 4461-4480
Published online Nov 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i41.4461
Published online Nov 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i41.4461
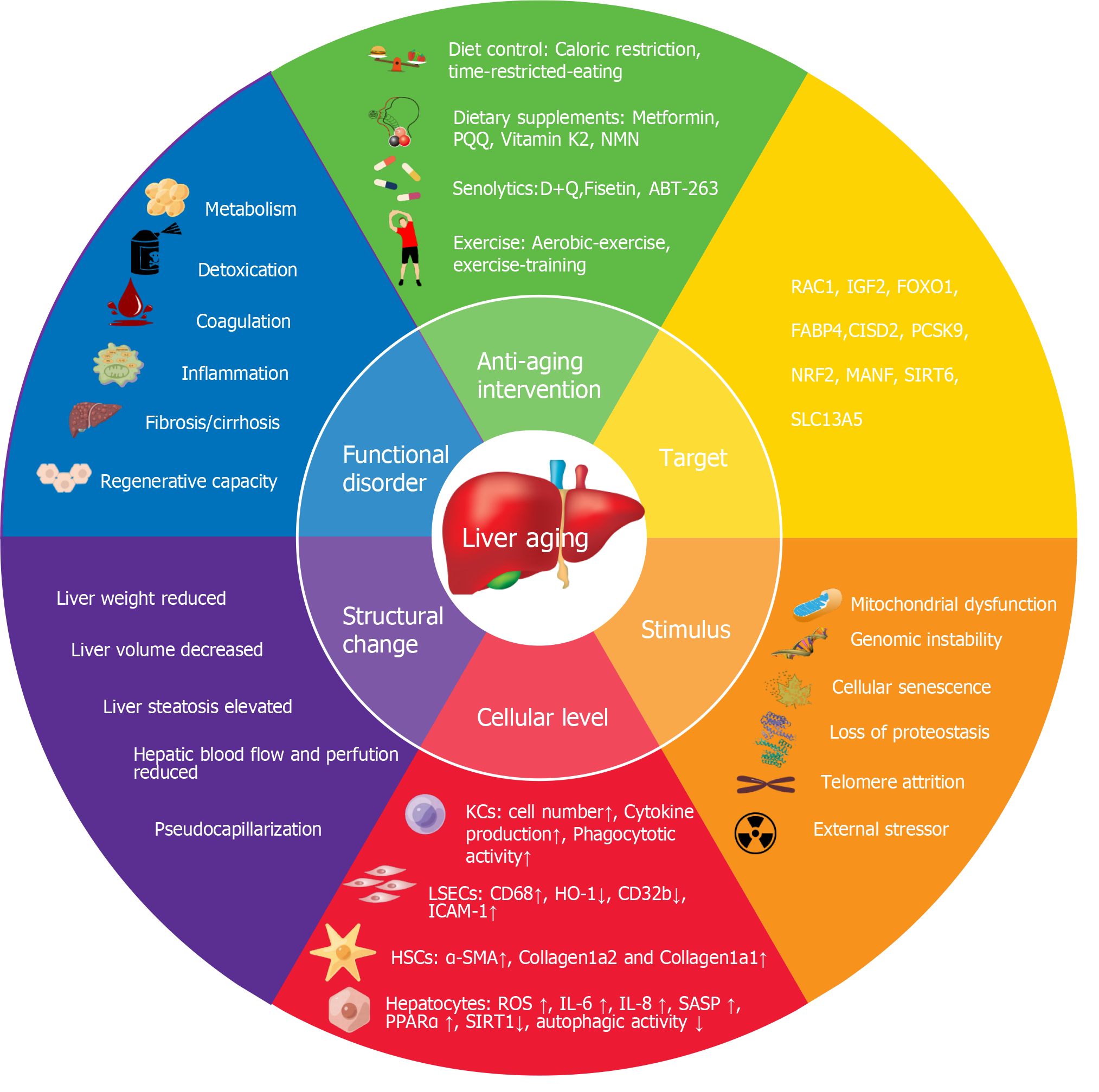
Figure 11 Holistic model in liver aging research.
The figure illustrates the stimuli of liver aging, cellular, structural and functional changes caused by liver aging, and interventions and targets for delaying liver aging. PQQ: Pyrroloquinoline quinone; NMN: Nicotinamide mononucleotide; FABP4: Fatty acid binding protein 4; RAC1, Ras-related C3 botulinum substrate 1; IGF2: Insulin-like growth factor 2; FOXO1: Forkhead box O1; CISD2: CDGSH iron–sulfur domain-containing protein 2; PCSK9: Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9; MANF: Mesencephalic-astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor; SIRT6: Sirtuin 6; SLC13A5: Solute carrier family 13 member 5; HO-1: Heme oxygenase 1; ICAM-1: Intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1; LSECs: Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells; HSCs: Hepatic stellate cells; α-SMA: Alpha-smooth muscle; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; KCs: Kupffer cells; DNMT1: DNA (cytosine-5-)- methyltransferase 1; D + Q: Dasatinib (D) and quercetin (Q); CD32b: Fc gamma receptor IIb; PPARα: Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha; SASP: Senescence-associated secretory phenotype; IL: Interleukin.
- Citation: Han QH, Huang SM, Wu SS, Luo SS, Lou ZY, Li H, Yang YM, Zhang Q, Shao JM, Zhu LJ. Mapping the evolution of liver aging research: A bibliometric analysis. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(41): 4461-4480
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i41/4461.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i41.4461