Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2024; 30(41): 4449-4460
Published online Nov 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i41.4449
Published online Nov 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i41.4449
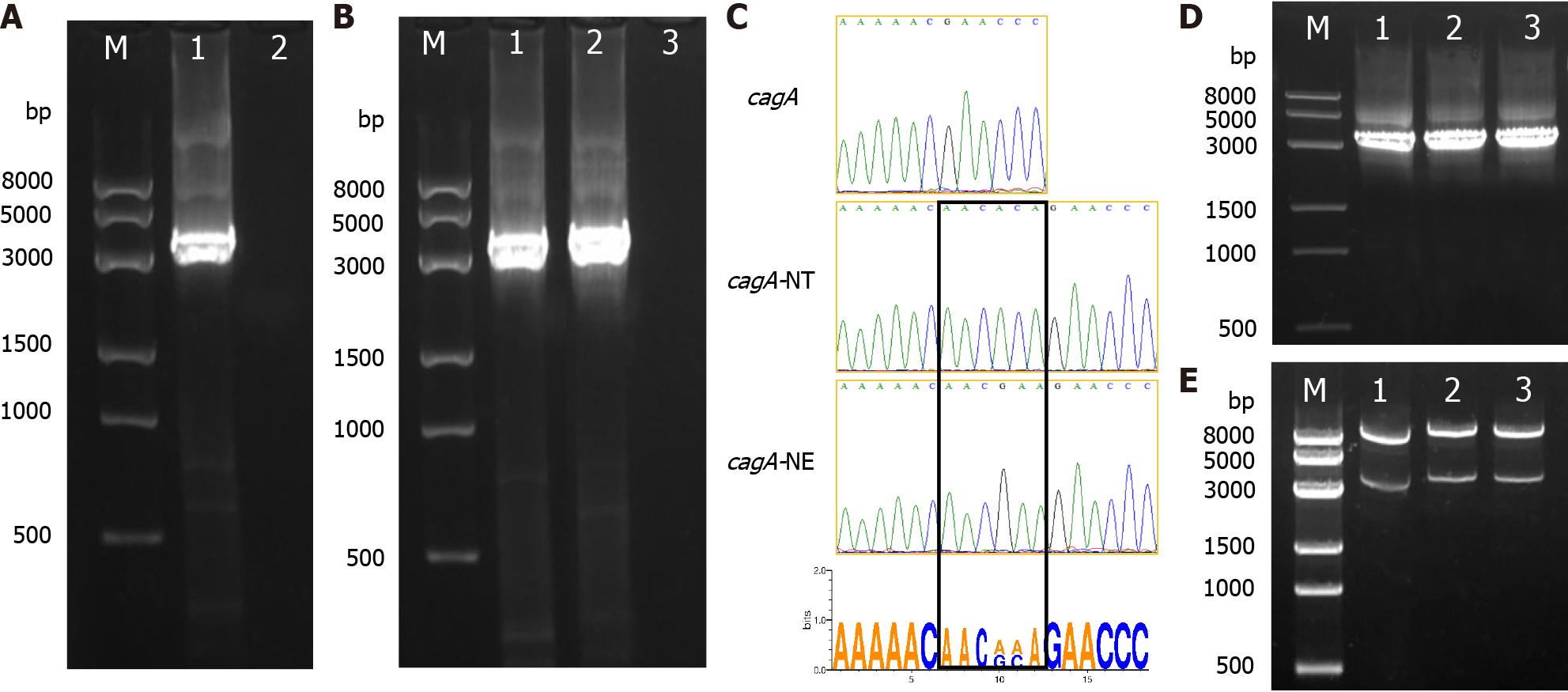
Figure 1 Identification of cytotoxin-associated gene A and its mutated genes.
A: The cytotoxin-associated gene A (cagA) gene was amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) from the HZT strain. Lane M: DNA marker; lane 1 cagA gene; lane 2 Control; B: The mutated gene was amplified by splicing by overlap extension (SOE) PCR. Lane M: DNA marker; lane 1 cagA-NT gene; lane 2 cagA-NE gene; lane 3 Control; C: Sanger sequencing results; D: The target genes were amplified by PCR from eukaryotic expression recombinant plasmids. Lane M: DL8000 DNA marker; lane 1 pAdtrack/cagA; lane 2 pAdtrack/cagA-NT; lane 3 pAdtrack/cagA-NE; E: Double enzyme identification results. Lane M: DL8000 DNA marker; lane 1 pAdtrack/cagA; lane 2 pAdtrack/cagA-NT; lane 3 pAdtrack/cagA-NE. cagA: Cytotoxin-associated gene A.
- Citation: Xue ZJ, Gong YN, He LH, Sun L, You YH, Fan DJ, Zhang MJ, Yan XM, Zhang JZ. Amino acid deletions at positions 893 and 894 of cytotoxin-associated gene A protein affect Helicobacter pylori gastric epithelial cell interactions. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(41): 4449-4460
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i41/4449.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i41.4449