Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2024; 30(4): 367-380
Published online Jan 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i4.367
Published online Jan 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i4.367
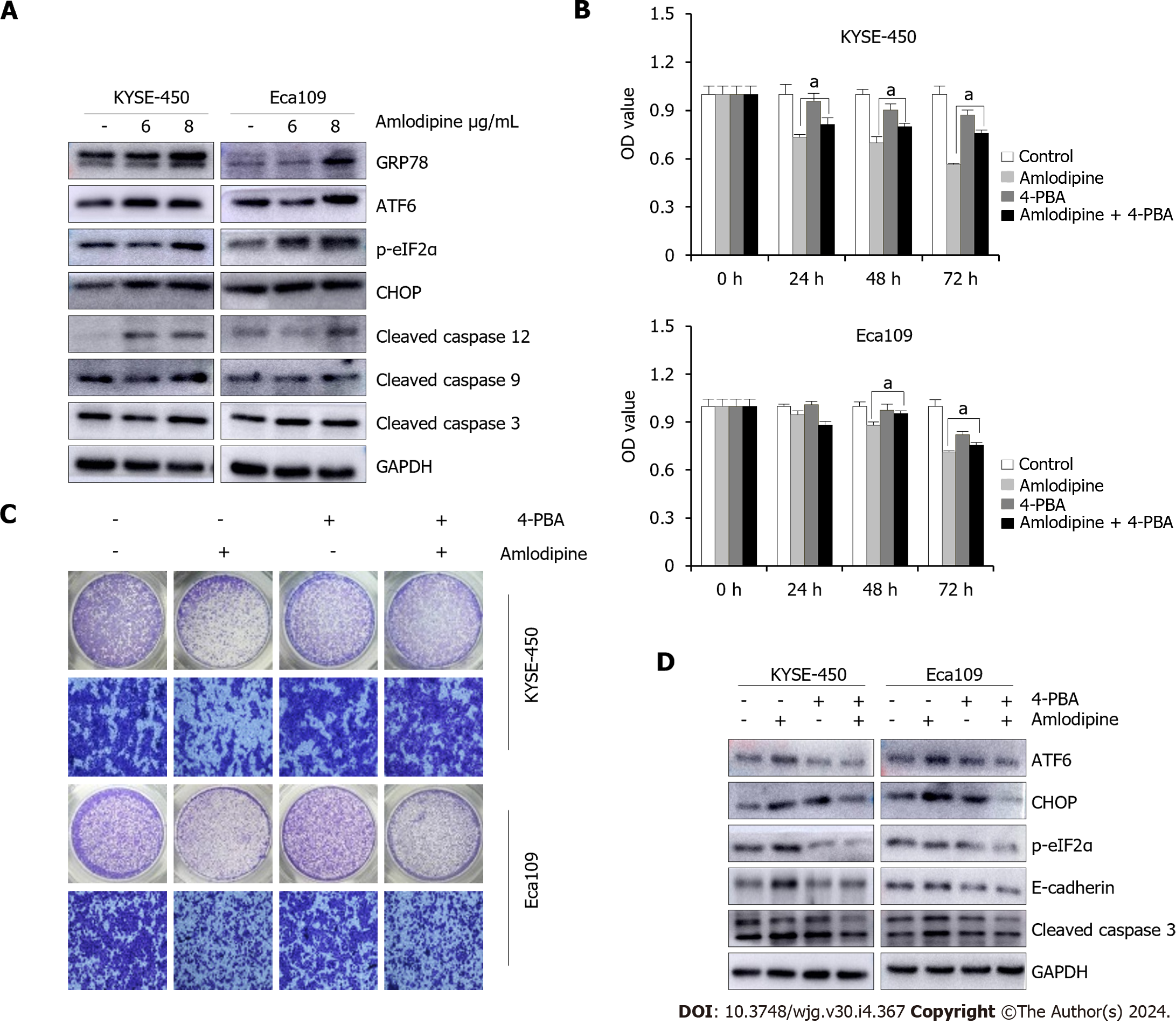
Figure 4 Amlodipine repressed esophageal carcinoma proliferation and migration via induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress.
A: KYSE-450 and Eca109 cells were treated with amlodipine at different concentrations for two days. According to the Western blot results, the protein levels of CHOP, p-eIF2α, GRP78, cleaved caspase-12, ATF6, cleaved caspase-9, and cleaved caspase-3 could be observed; B: With a concentration of 4 μg/mL amlodipine drug, 0.2 μM of 4-phenylbutyric acid (4-PBA), mixed treatment, then placed into KYSE-450 and Eca109 cells, with the help of 3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay to test the cell activity presented by these cells in 1 d to 3 d aP < 0.05 vs amlodipine; C: Transwell migration assay was conducted to examine cell migration of KYSE-450 and Eca109 when treatment with amlodipine (4 μg/mL), 4-PBA (0.2 μM) or both combination for 24 h; D: Western blot analysis showed the levels of ATF6, CHOP, p-eIF2α, E-cadherin, and cleaved caspase-3 in KYSE-450 and Eca109 cells after treatment with amlodipine (4 μg/mL), 4-PBA (0.2 μM) or both combination for 48 h. All amlodipine and 4-PBA combination treatment was applying 4-PBA in advance for 1 h then amlodipine.
- Citation: Chen YM, Yang WQ, Gu CW, Fan YY, Liu YZ, Zhao BS. Amlodipine inhibits the proliferation and migration of esophageal carcinoma cells through the induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(4): 367-380
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i4/367.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i4.367