Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2024; 30(39): 4308-4312
Published online Oct 21, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i39.4308
Published online Oct 21, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i39.4308
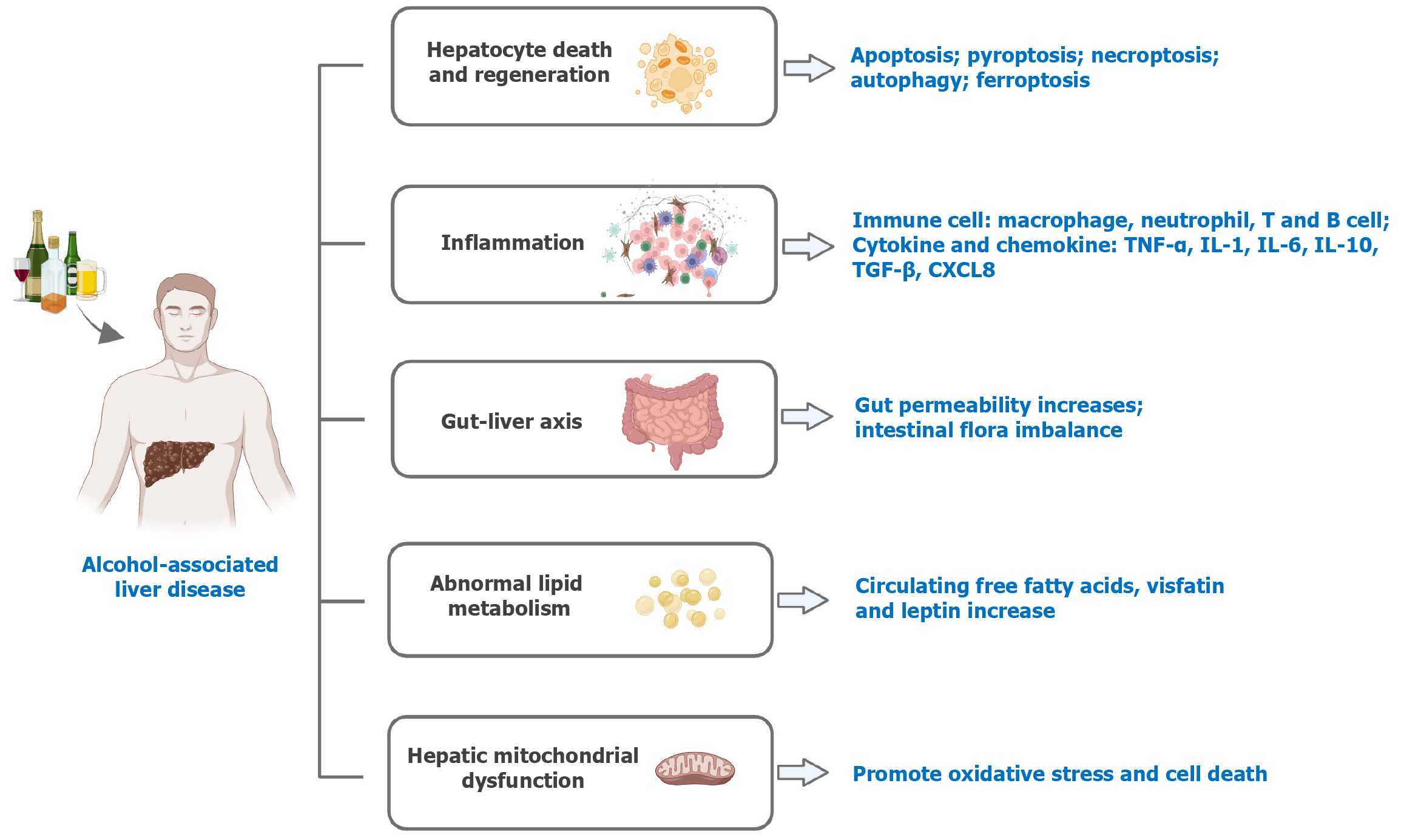
Figure 1 Pathogeneses of alcohol-associated liver disease.
The primary mechanisms involved in the development of alcohol-associated liver disease are listed. Cell death and regeneration, inflammation, the gut-liver axis, lipid metabolism, and mitochondrial dysfunction all contribute to the development of alcohol-associated liver disease. Created with BioRender.com. TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; IL: Interleukin; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-β.
- Citation: Gao FQ, Zhu JQ, Feng XD. Novel intervention for alcohol-associated liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(39): 4308-4312
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i39/4308.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i39.4308