Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2024; 30(34): 3894-3925
Published online Sep 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i34.3894
Published online Sep 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i34.3894
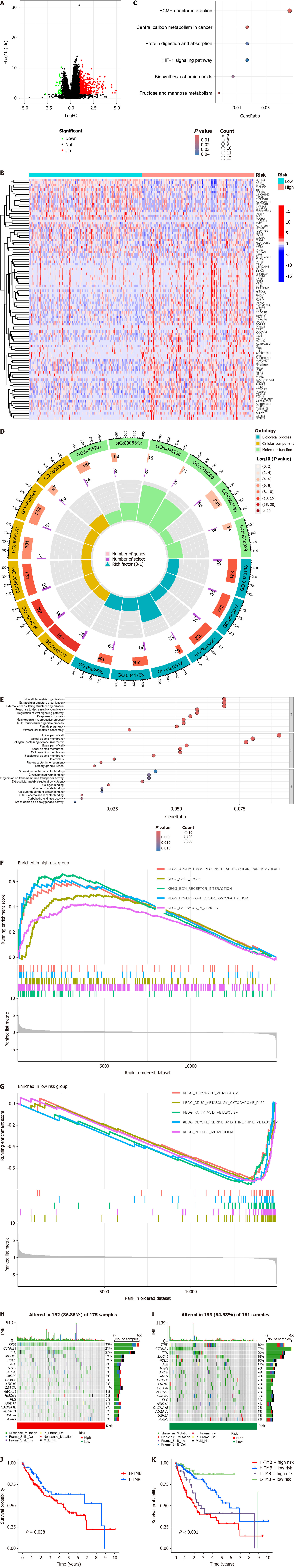
Figure 7 Functional enrichment analysis of different risk score groups.
A: Heatmap displays the expression levels of the top 50 differentially expressed genes across different risk score groups in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) samples; B: Volcano plot illustrates the differentially expressed genes across different risk score groups. Red indicates fold change > 2, false discovery rate (FDR) < 0.05; green indicates fold change < 2, FDR < 0.05; C: Bubble plot presents the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway enrichment analysis results across different risk score groups; D: Bubble plot demonstrates gene ontology (GO) enrichment analysis pathways and proportions across different risk score groups; E: Bubble plot exhibits GO enrichment analysis pathways, number of genes, and their statistical significance across different risk score groups; F: Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) analysis reveals the key pathways enriched in HCC patients with high risk scores; G: GSEA analysis unveils the key pathways enriched in HCC patients with low risk scores; H: Somatic mutation data analysis showcases the mutation rates of key genes in HCC patients with high risk scores; I: Somatic mutation data analysis displays the mutation rates of key genes in HCC patients with low risk scores; J: Survival analysis illustrates the prognosis of HCC patients in different tumor mutation burden groups; K: Survival analysis demonstrates the impact of tumor mutation burden combined with risk score groups on the prognosis of HCC patients. FC: Fold change; ECM: Extracellular matrix; HIF: Hypoxia-inducible factor; KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes.
- Citation: Xu KQ, Gong Z, Yang JL, Xia CQ, Zhao JY, Chen X. B-cell-specific signatures reveal novel immunophenotyping and therapeutic targets for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(34): 3894-3925
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i34/3894.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i34.3894