Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2024; 30(34): 3894-3925
Published online Sep 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i34.3894
Published online Sep 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i34.3894
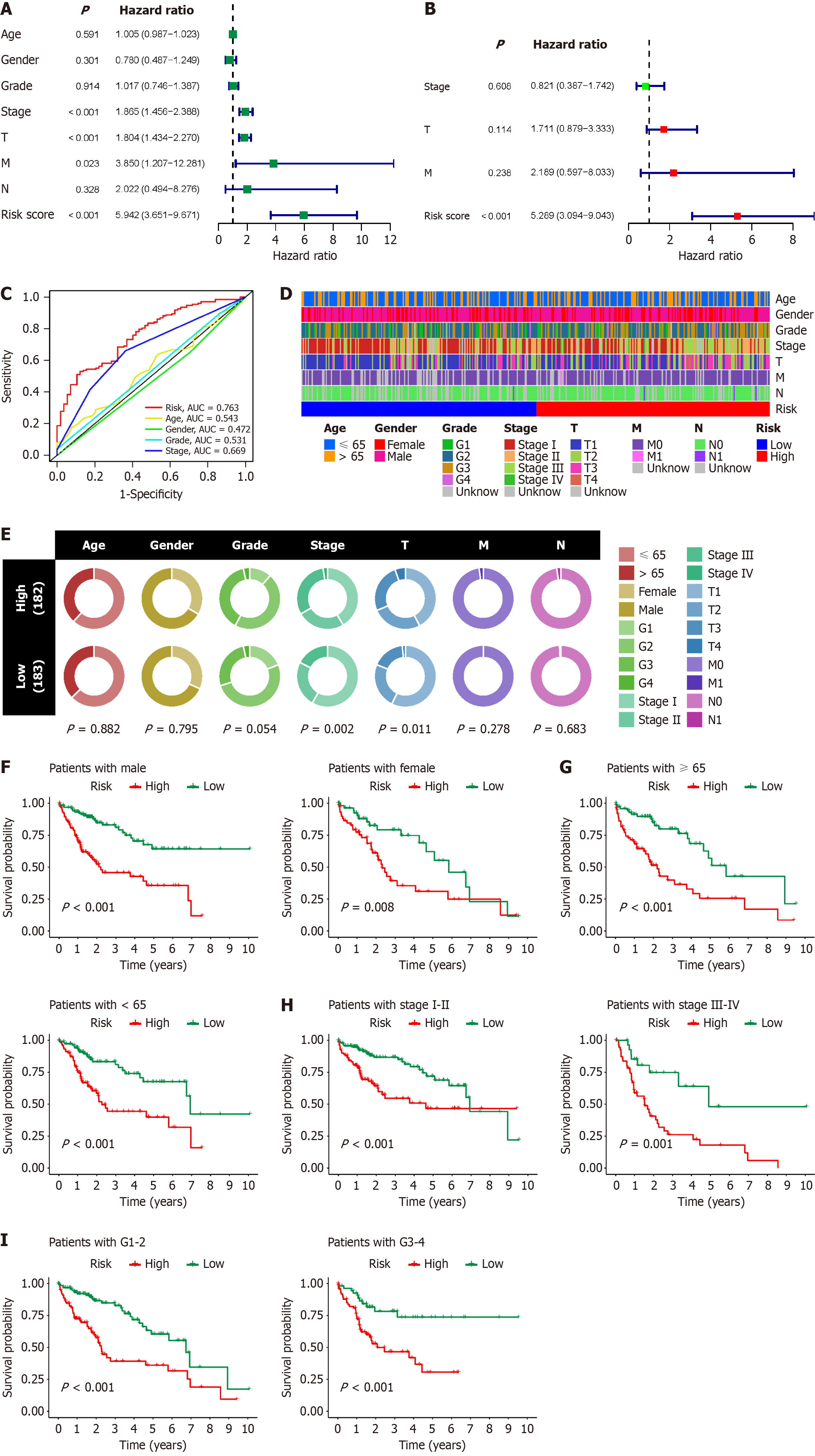
Figure 6 Clinical correlation analysis of B-cell-related genes prognostic model in hepatocellular carcinoma.
A: Single-factor Cox regression analysis shows the association between risk score and other clinicopathological factors of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with prognosis; B: Multifactor Cox regression analysis demonstrates whether risk score and other clinicopathological factors of HCC can serve as independent prognostic factors for HCC; C: Receiver operating characteristic curve illustrates the effectiveness of risk score and other clinicopathological factors of HCC in predicting the prognosis of HCC patients; D: Heatmap displays the distribution of various clinical and pathological statuses of HCC patients in different risk score groups; E: Bubble plot demonstrates the proportions of various clinical and pathological statuses among HCC patients in different risk score groups and their correlation with risk score; F–I: Survival analysis shows the ability of the B-cell-related genes prognostic model to predict the prognosis of HCC patients in various clinical subgroups. AUC: Areas under the curves.
- Citation: Xu KQ, Gong Z, Yang JL, Xia CQ, Zhao JY, Chen X. B-cell-specific signatures reveal novel immunophenotyping and therapeutic targets for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(34): 3894-3925
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i34/3894.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i34.3894