Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2024; 30(34): 3894-3925
Published online Sep 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i34.3894
Published online Sep 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i34.3894
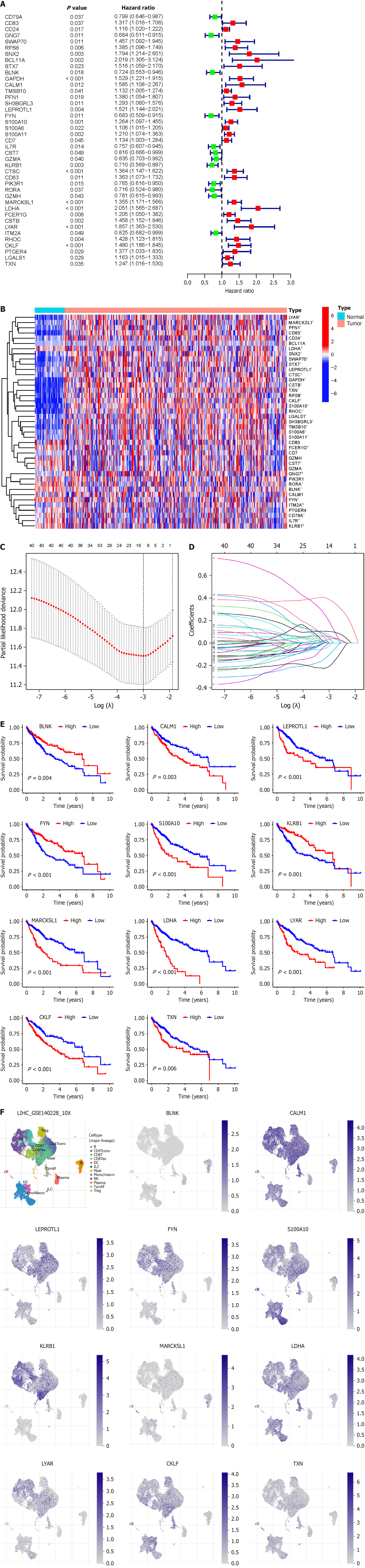
Figure 4 Establishment of prognostic model of B-cell-related genes in hepatocellular carcinoma.
A: Forest plot displays B-cell-related genes (BRGs) associated with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) prognosis, green indicates hazard ratio < 1, red indicates hazard ratio > 1; B: Heatmap illustrates the expression levels of BRGs associated with HCC prognosis in both HCC and paired adjacent non-tumor samples; C: Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression analysis cross-validation curve demonstrates the fitting effect of the model when incorporating different numbers of BRGs; D: LASSO coefficient path plot displays the lambda values when the model incorporates different numbers of BRGs; E: Survival analysis depicts the relationship between the expression levels of 11 BRGs included in the prognostic model and the prognosis of HCC patients; F: Single-cell analysis reveals the expression levels of the 11 BRGs included in the prognostic model within B cells of HCC. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001.
- Citation: Xu KQ, Gong Z, Yang JL, Xia CQ, Zhao JY, Chen X. B-cell-specific signatures reveal novel immunophenotyping and therapeutic targets for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(34): 3894-3925
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i34/3894.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i34.3894