Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2024; 30(33): 3810-3817
Published online Sep 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i33.3810
Published online Sep 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i33.3810
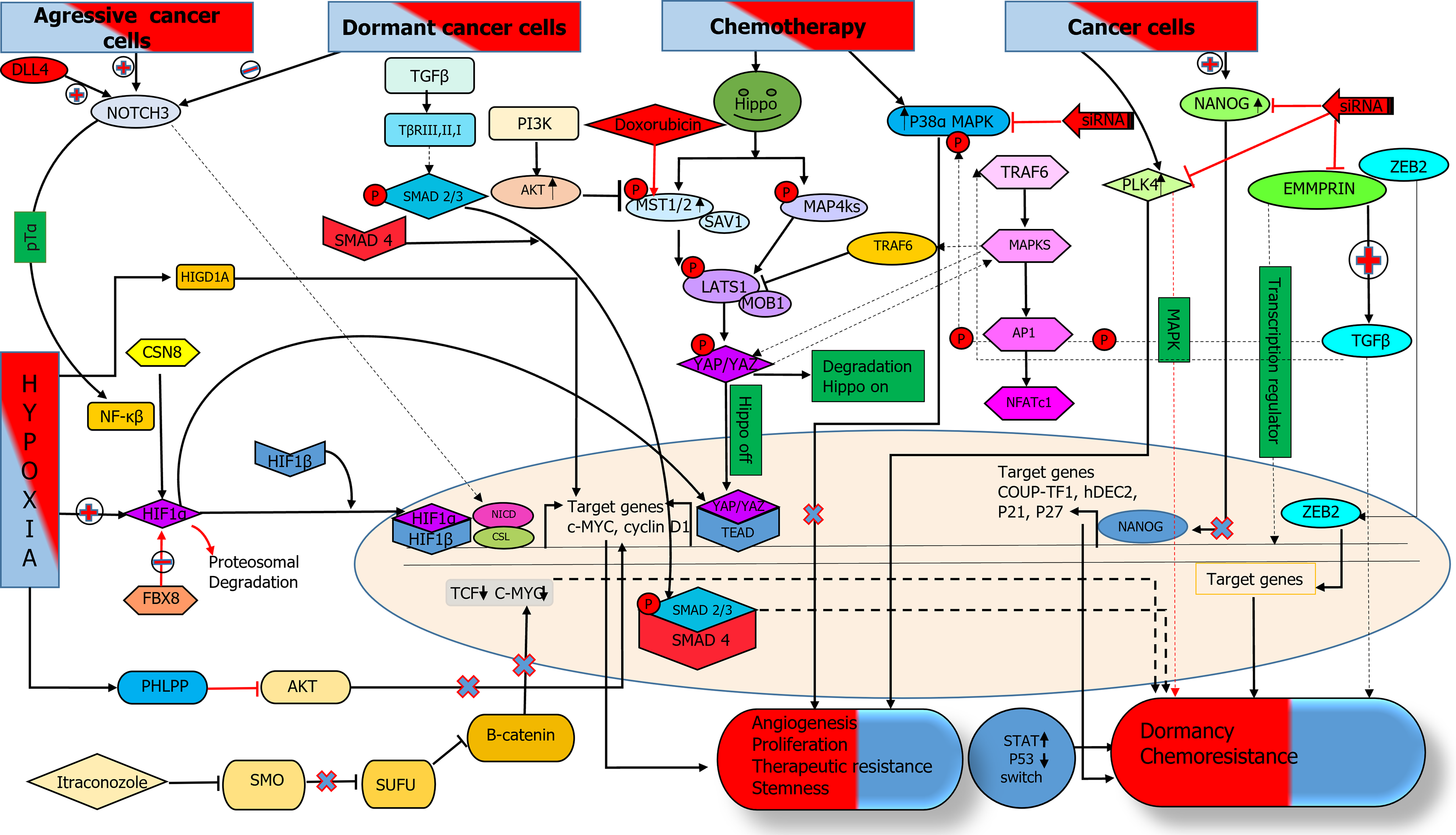
Figure 1 Various signaling pathways implicated in driving cancer cells into dormancy, along with interactions between these pathways and their associated molecules or markers.
Notch signaling exhibits variable expression, being elevated in aggressive cancer cells and reduced in dormant ones. Notch 3, with CSN8, activates NF-κB signaling, increasing HIF1α expression under low oxygen or stress, which promotes proliferation and angiogenesis. HIF1α either partners with HIF1β to drive gene expression in the nucleus or enhances YAP/TAZ-TEAD interaction, both supporting growth and angiogenesis. This suggests that Hippo pathway activation induces dormancy, while HIF1α signaling is reduced during dormancy. Conversely, the FBX8 F-box protein degrades HIF1α, increasing dormancy marker expression. It is still a question of how HIF1α regulates both proliferation and dormancy concurrently. Hypoxic conditions increase PHLPP expression, blocking AKT signaling and boosting dormancy markers while reducing proliferation markers in dormant colorectal cancer (CRC) cells. AKT and MAPKs negatively regulate Hippo signaling and promote YAP/TAZ nuclear translocation by inhibiting MST1/2/SAV1 and LATS1/MOB1 complexes, respectively. Dormant CRC cells show decreased AKT and increased MAPK expression. HIGD1A, a hypoxia-induced factor, typically promotes cancer cell proliferation under stress but induces tumor dormancy in deeper cancer tissues. TGFβ/SMAD signaling drives cancer cell dormancy, while the MAPK pathway, via increased P38α expression, regulates the switch between proliferation and dormancy in CRC and cancer cell dormancy. Downregulation of P38α leads to growth arrest, and PLK4, a key proliferation regulator, decreases in dormant CRC cells driven by MAPK signaling. Itraconazole regulates the non-canonical WNT pathway in CRC dormancy by inhibiting smoothened, activating suppressor of fused, and ultimately inhibiting β-catenin, temporarily inducing a brief growth cycle before permanent arrest. EMMPRIN inhibition promotes dormancy, while NANOG and ZEB increase dormancy marker expression, making all three dormancy markers. SMO: Smoothened; SUFU: Suppressor of fused.
- Citation: Kumar A, Saha L. Colorectal cancer cell dormancy: An insight into pathways. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(33): 3810-3817
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i33/3810.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i33.3810