Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2024; 30(31): 3689-3704
Published online Aug 21, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i31.3689
Published online Aug 21, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i31.3689
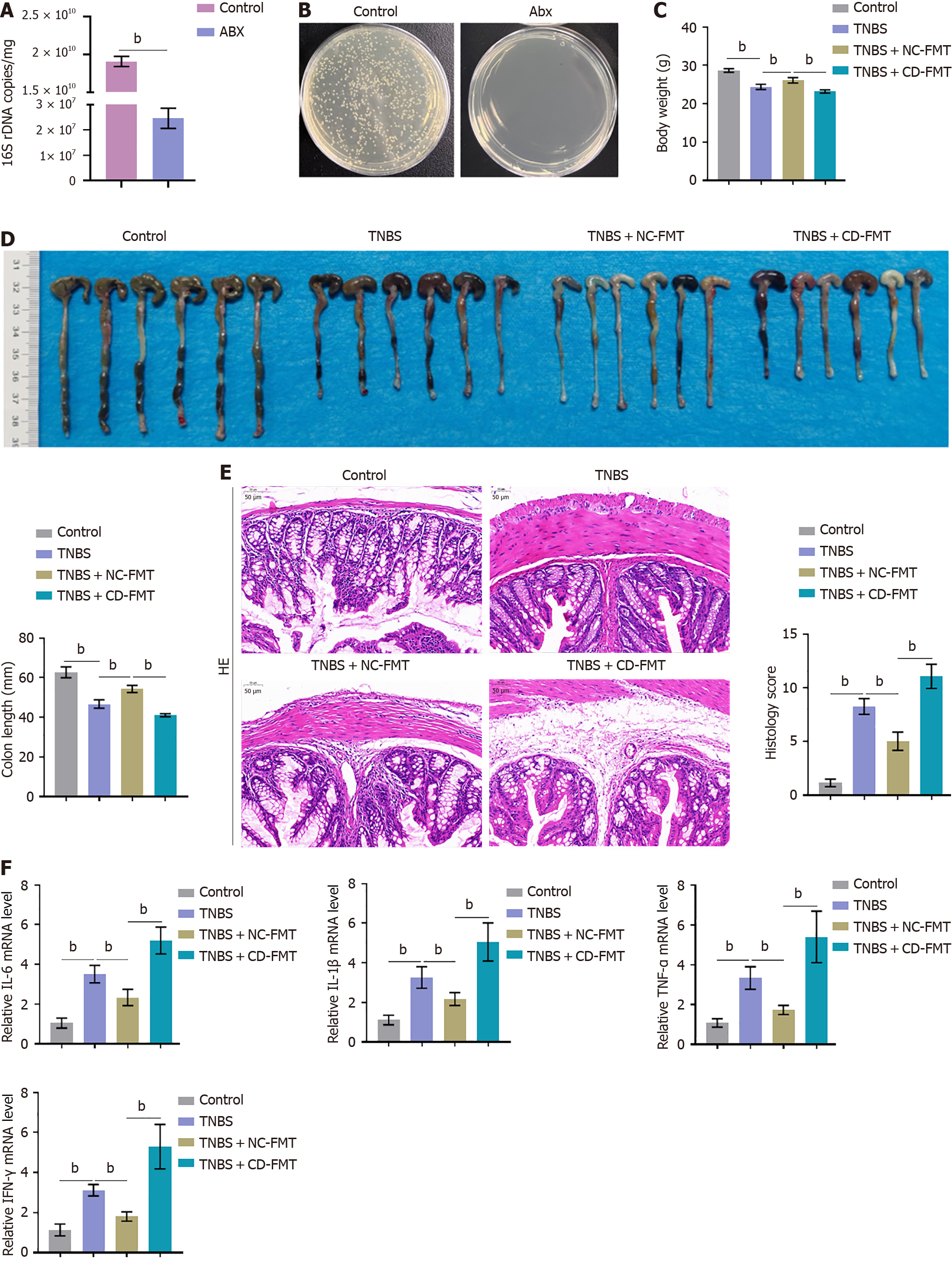
Figure 2 Fecal microbiota transplantation into mice with 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced Crohn’s disease.
A and B: Mice were subjected to antibiotic cleaning to achieve a pseudo germ-free intestinal environment, with the results verified by 16S rRNA sequencing. n = 6. bP < 0.01 by unpaired t-tests; C and D: 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS)-treated mice underwent fetal microbiota transplantation (FMT) from clinically healthy donors or Crohn’s disease patients, and their body weights and colon lengths were monitored; E: Evaluation of histopathological alterations in colon samples by hematoxylin-eosin staining and evaluation of histology scores (× 150); F: Real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction assays of interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-1β, tumour necrosis factor alpha, and interferon-gamma mRNA expression levels in colon tissue samples. n = 6, bP < 0.01 vs control; bP < 0.01 vs TNBS alone; bP < 0.01 vs TNBS + healthy donor (NC)-FMT, by one-way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey HSD test. Abx: Antibiotics; TNBS: 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid; CD: Crohn’s disease; NC: Normal control; FMT: Fetal microbiota transplantation; IFN-γ: Interferon-gamma; TNF-α: Tumour necrosis factor alpha; IL: Interleukin.
- Citation: Wu Q, Yuan LW, Yang LC, Zhang YW, Yao HC, Peng LX, Yao BJ, Jiang ZX. Role of gut microbiota in Crohn’s disease pathogenesis: Insights from fecal microbiota transplantation in mouse model. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(31): 3689-3704
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i31/3689.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i31.3689