Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2024; 30(31): 3654-3667
Published online Aug 21, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i31.3654
Published online Aug 21, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i31.3654
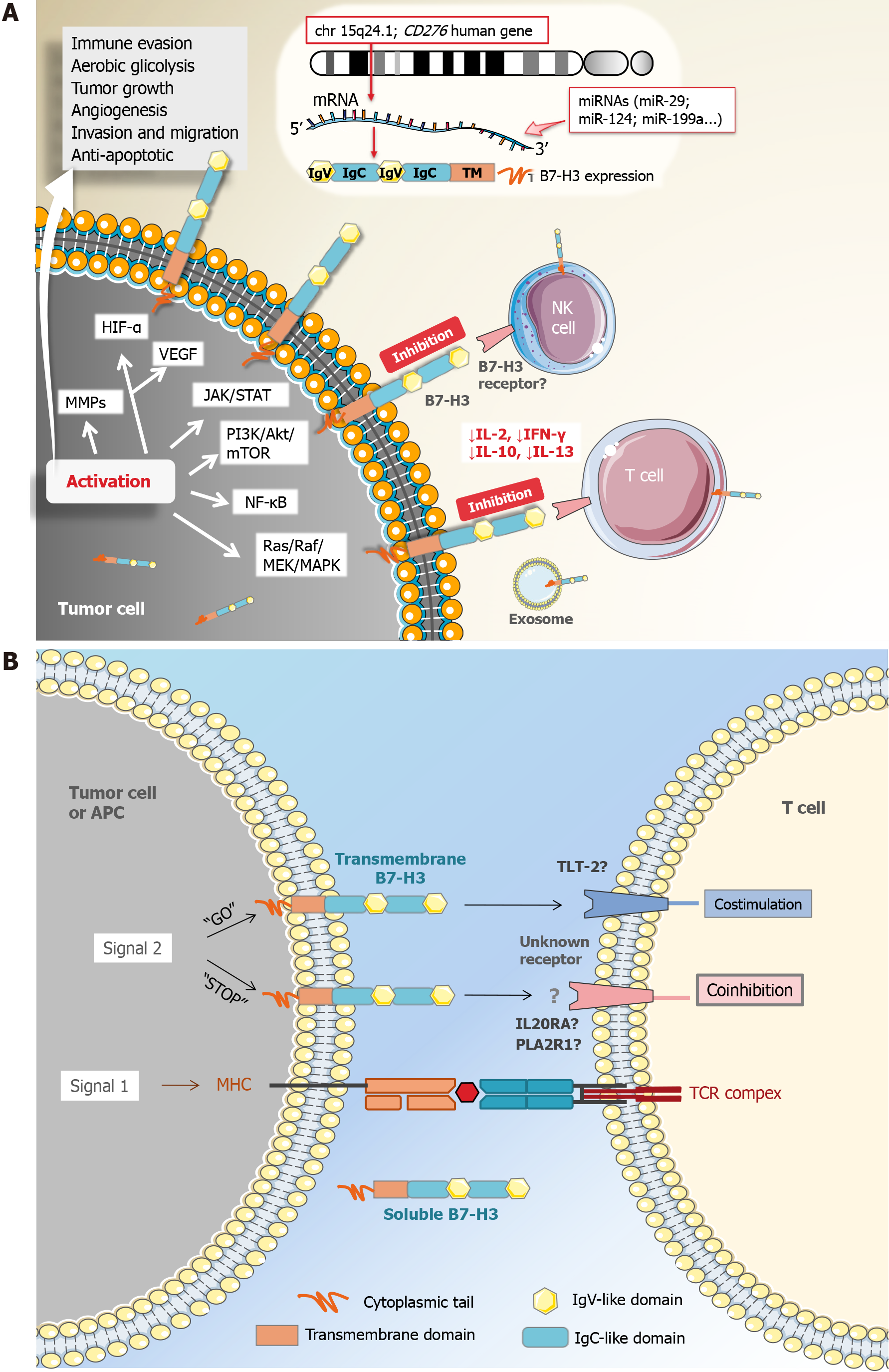
Figure 1 B7 homolog 3.
A: Regulation of B7 homolog 3 (B7-H3) expression and its immunological and nonimmunological tumor-promoting molecular mechanisms; B: Role of B7-H3 in T cell activation. Although some studies recognize B7-H3 as a costimulatory molecule, most available data evidence its coinhibitory role. The B7-H3 receptor(s) is still unknown. Three possible receptors have been suggested to date, namely triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-like transcript 2 possibly conducting costimulatory signal, and interleukin 20 receptor subunit alpha, and phospholipase A2 receptor 1 possibly conducting coinhibitory signal. Akt: Protein kinase B; APC: Antigen-presenting cell; B7-H3: B7 homolog 3; CD276: Cluster of differentiation 276, chr: Chromosome; HIF-α: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha; IFN-γ: Interferon-gamma; IgC: Immunoglobulin constant region; IgV: Immunoglobulin variable region; IL-2: Interleukin-2; IL-10: Interleukin-10; IL-13: Interleukin-13; JAK: Janus kinase; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase, MEK: MAPK kinase; miRNAs: MicroRNAs; MMPs: Matrix metalloproteinases; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappa B; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; MHC: Major histocompatibility complex; TCR: T cell receptor. This Figure was partly generated using images from Servier Medical Art, provided by Servier (https://smart.servier.com/smart_image/), licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 international license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/) (Supplementary material).
- Citation: Perovic D, Dusanovic Pjevic M, Perovic V, Grk M, Rasic M, Milickovic M, Mijovic T, Rasic P. B7 homolog 3 in pancreatic cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(31): 3654-3667
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i31/3654.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i31.3654