Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2024; 30(30): 3584-3608
Published online Aug 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i30.3584
Published online Aug 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i30.3584
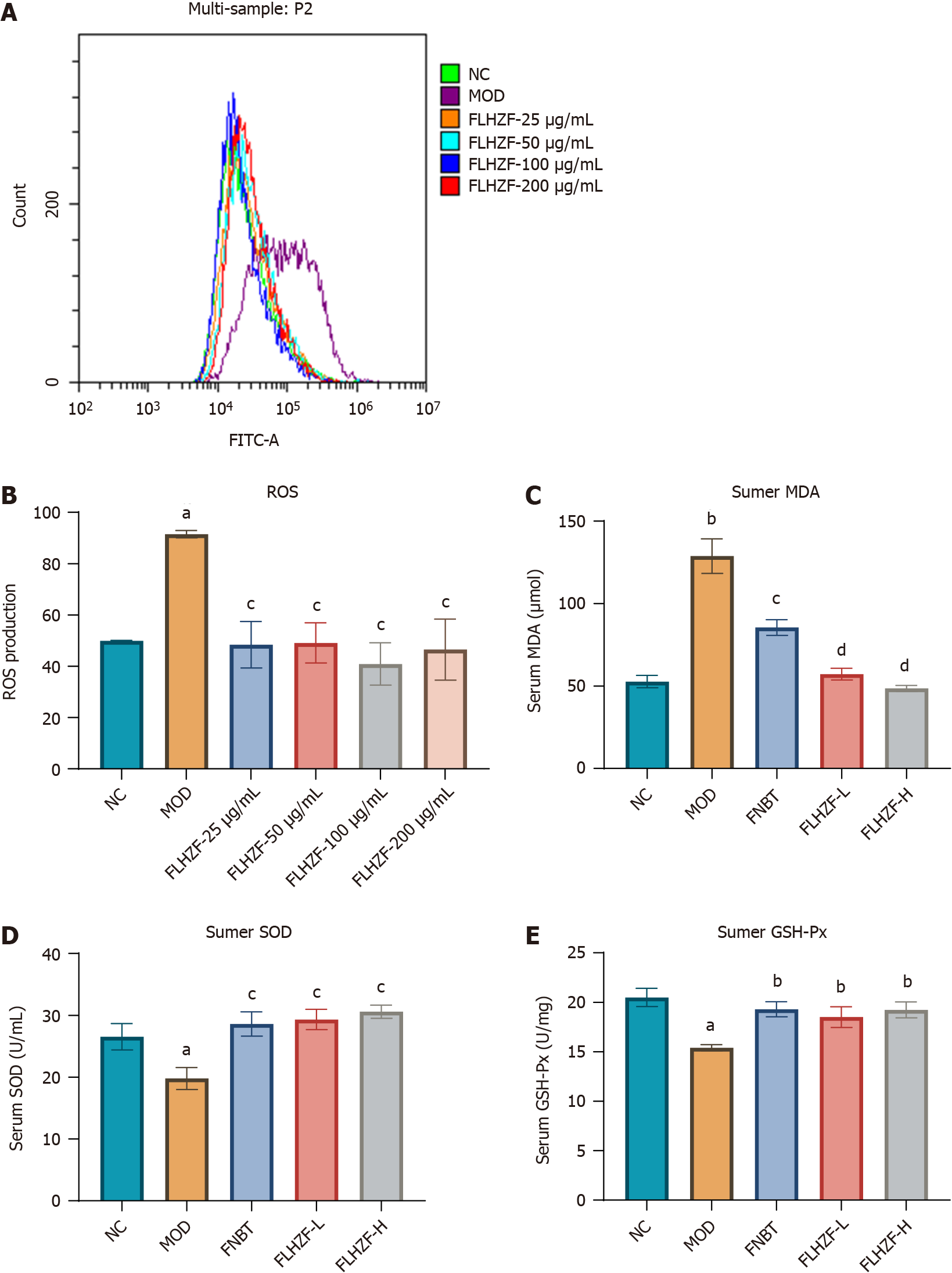
Figure 4 Fanlian Huazhuo Formula group reduced oxidative damage in vivo and in vitro.
A: Cell reactive oxygen species (ROS) content with Fanlian Huazhuo Formula group treatment in HepG2 cells induced by free fatty acid (n = 3); B: Quantitative result of cell ROS content (n = 3); C: Serum levels of malondialdehyde (n = 8); D: Serum levels of superoxide dismutase (n = 8); E: Serum levels of glutathione peroxidase (n = 8). Data are presented as mean ± SE. aP < 0.05 vs NC group, bP < 0.01 vs NC group, cP < 0.05 vs MOD group, dP < 0.01 vs MOD group. ROS: Reactive oxygen species; MDA: Malondialdehyde; SOD: Superoxide dismutase: GSH-Px: Glutathione peroxidase; NC: Negative control group; MOD: Model group; FNBT: Fenofibrate group; FLHZF-L: Low dose of Fanlian Huazhuo Formula group; FLHZF-H: High dose of Fanlian Huazhuo Formula group.
- Citation: Niu MY, Dong GT, Li Y, Luo Q, Cao L, Wang XM, Wang QW, Wang YT, Zhang Z, Zhong XW, Dai WB, Li LY. Fanlian Huazhuo Formula alleviates high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by modulating autophagy and lipid synthesis signaling pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(30): 3584-3608
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i30/3584.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i30.3584