Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2024; 30(29): 3511-3533
Published online Aug 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i29.3511
Published online Aug 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i29.3511
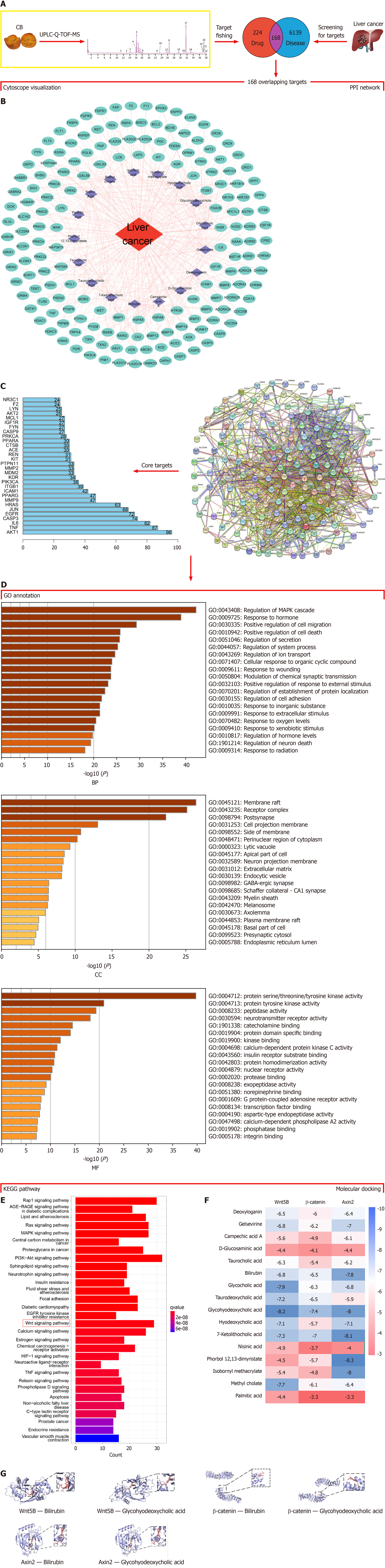
Figure 3 Cyberpharmacological study on anti-liver cancer mechanism of active components of Calculus bovis based on UPLC-Q-TOF-MS analysis.
A: Intersection plot of potential targets of Calculus bovis (CB) and liver cancer targets; B: Component-target-disease interaction network of CB against liver cancer. The purple quadrilaterals represent the active components of CB; C: Protein-protein interaction network; D: Gene Ontology function analysis of CB against liver cancer; E: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway enrichment analysis of CB against liver cancer; F: Minimum binding energy of the active components of CB with core target proteins; G: Molecular docking diagram of some active components.
- Citation: Huang Z, Meng FY, Lu LZ, Guo QQ, Lv CJ, Tan NH, Deng Z, Chen JY, Zhang ZS, Zou B, Long HP, Zhou Q, Tian S, Mei S, Tian XF. Calculus bovis inhibits M2 tumor-associated macrophage polarization via Wnt/β-catenin pathway modulation to suppress liver cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(29): 3511-3533
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i29/3511.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i29.3511