Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2024; 30(29): 3488-3510
Published online Aug 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i29.3488
Published online Aug 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i29.3488
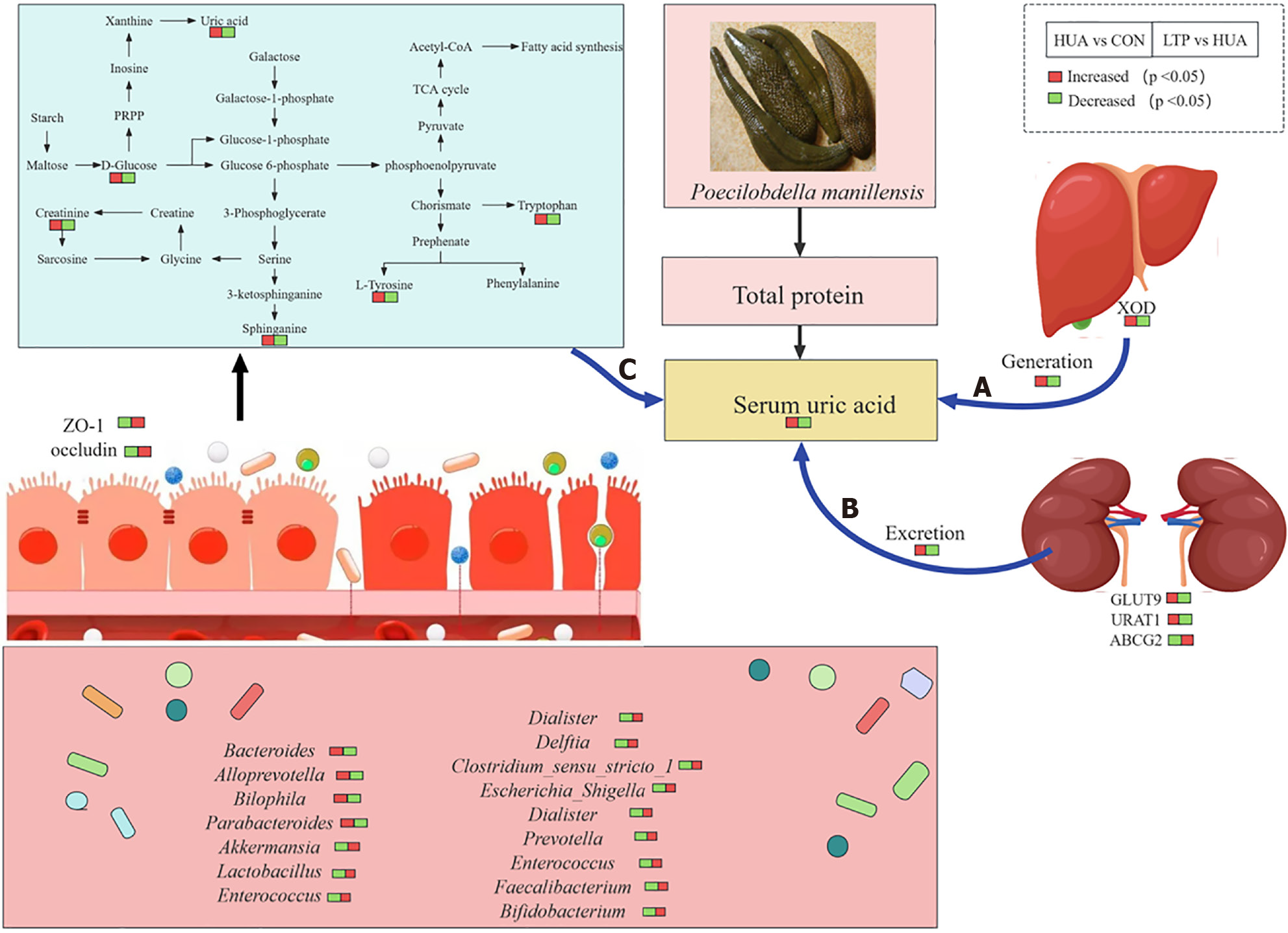
Figure 10 Mechanisms associated with treatment of Poecilobdella manillensis for hyperuricemia.
A: decreased of uric acid generation in liver by reducing levels of xanthine oxidase; B: Reduction of uric acid excretion from kidney by regulating the expression of glucose transporter 9, urate transporter 1, and ATP-binding cassette transporter G2; C: Improvement of gut microbiota dysbiosis and regulation of sphingolipid metabolism and galactose metabolism. CON: Normal control group; HUA: Hyperuricemia model group; LTP: Leech Poecilobdella manillensis total protein extract treatment group; ZO-1: Zonula occludens-1; URAT1: Urate transporter 1; GLUT9: Glucose transporter 9; ABCG2: ATP-binding cassette transporter G2; XOD: Xanthine oxidase.
- Citation: Liu X, Liang XQ, Lu TC, Feng Z, Zhang M, Liao NQ, Zhang FL, Wang B, Wang LS. Leech Poecilobdella manillensis protein extract ameliorated hyperuricemia by restoring gut microbiota dysregulation and affecting serum metabolites. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(29): 3488-3510
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i29/3488.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i29.3488