Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2024; 30(28): 3428-3446
Published online Jul 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i28.3428
Published online Jul 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i28.3428
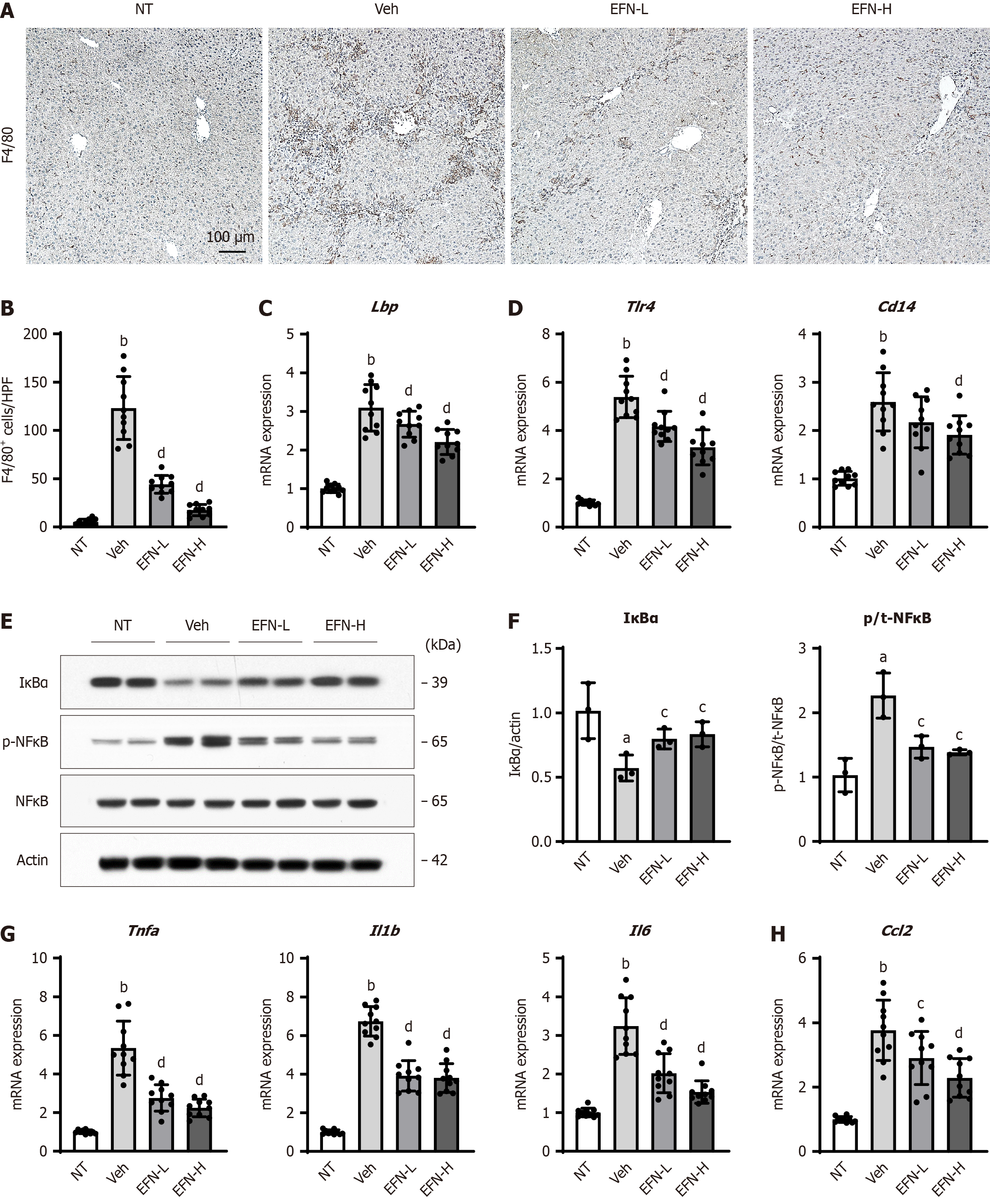
Figure 5 Elafibranor on Kupffer cell-mediated inflammatory response in the alcohol-associated liver disease mice.
A: Representative microphotographs of F4/80 staining of the livers in the experimental mice; B: Quantification of F4/80-positive cells in high-power field (n = 10); C and D: Hepatic mRNA level of lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (C), toll like receptor 4 and CD14 (D) (n = 10); E: Western blot for the protein expression of IκBα, p-nuclear factor kappa B (NFκB) and NF-κB in the liver tissue. Actin was used as an internal control; F: Quantification of the protein level of IκBα and the ratio of NF-κB phosphorylation based on western blotting (n = 10); G and H: Hepatic mRNA level of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin 1β (Il1b), and Il6 (G), and Ccl2 (H) (n = 10). Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase was used as an internal control for real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (C, D, G and H). Quantitative values are indicated as fold changes to the values of non-therapeutic group. Data are the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05 vs non-therapeutic group; bP < 0.01 vs non-therapeutic group; cP < 0.05 vs vehicle-treated alcohol-associated liver disease group; dP < 0.01 vs vehicle-treated alcohol-associated liver disease group, significant difference between groups by Student’s t-test. NT: Non-therapeutic group; Veh: Vehicle-treated alcohol-associated liver disease group; EFN-L: Elafiblanor (3 mg/kg/day)-treated alcohol-associated liver disease group; EFN-H: Elafibranor (10 mg/kg/day)-treated alcohol-associated liver disease group; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; Lbp: Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein; TLR: Toll like receptor; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; IL: Interleukin.
- Citation: Koizumi A, Kaji K, Nishimura N, Asada S, Matsuda T, Tanaka M, Yorioka N, Tsuji Y, Kitagawa K, Sato S, Namisaki T, Akahane T, Yoshiji H. Effects of elafibranor on liver fibrosis and gut barrier function in a mouse model of alcohol-associated liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(28): 3428-3446
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i28/3428.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i28.3428