Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2024; 30(24): 3120-3122
Published online Jun 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i24.3120
Published online Jun 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i24.3120
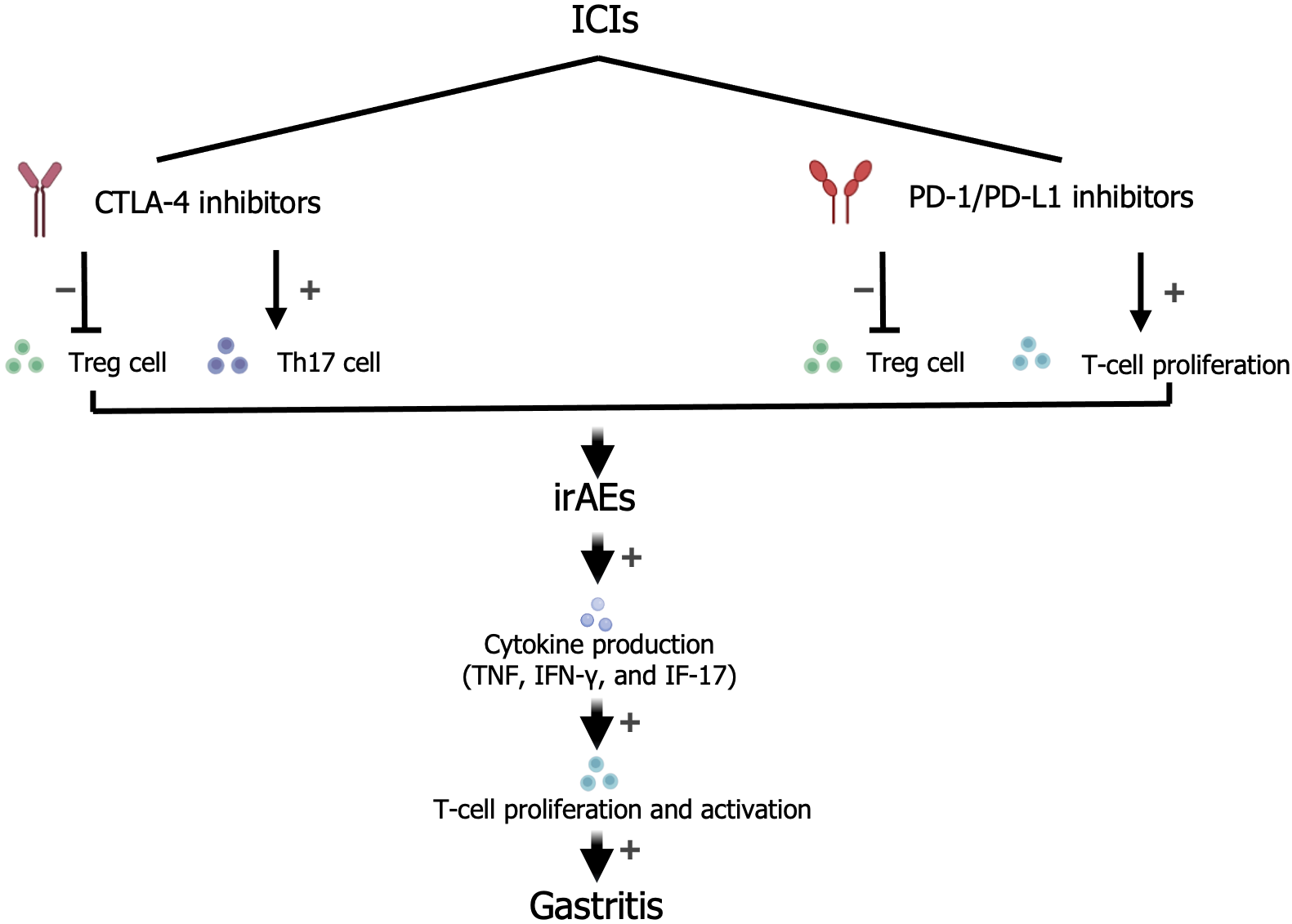
Figure 1 A common mechanism by which immune checkpoint inhibitors exert their effects involves activation of effector T cells by inhibition of programmed death 1, programmed death-ligand 1, and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4.
ICI: Immune checkpoint inhibitor; PD-1: Programmed death 1; PD-L1: Programmed death-ligand 1; CTLA-4: Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4; irAEs: Immune-related adverse events.
- Citation: Yu LL, He ZL, Qian XL. Managing immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated gastritis: Insights and strategies. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(24): 3120-3122
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i24/3120.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i24.3120