Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2024; 30(21): 2817-2826
Published online Jun 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i21.2817
Published online Jun 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i21.2817
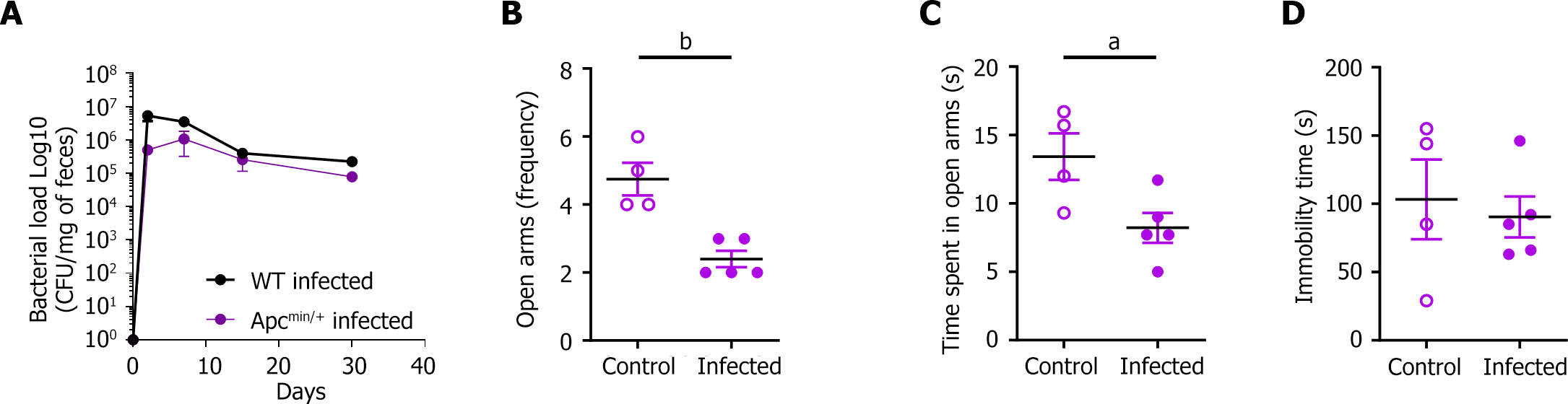
Figure 5 Chronic colibactin-producing Escherichia coli infection is associated with anxiety-like behaviors in adenomatous polyposis colimultiple intestinal neoplasia/+ mice.
A: Colonization of the gastrointestinal tract in wild-type (WT, n = 12) and adenomatous polyposis coli (Apc)multiple intestinal neoplasia (Min)/+ (n = 5) mice infected with the colibactin-producing Escherichia coli strain (11G5 strain) according to fecal colony form units at different time points; B and C: Anxiety-like behavior was assessed using an elevated plus maze test at 14 DPI. Entry frequency (B) and time spent in the open arms (C) by APCMin/+ control (n = 4) and infected (n = 5) mice; D: Immobility time during the forced swimming test of APCMin/+ control and infected mice at 35 DPI. The black circles represent WT infected mice, the hollow purple circles represent APCMin/+ uninfected mice, and the purple circles represent APCMin/+ infected mice. Statistical analysis: Student’s t test: aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. CFU: Colony form unit; APC: Adenomatous polyposis coli; Min: Multiple intestinal neoplasia; WT: Wild-type.
- Citation: Rondepierre F, Meynier M, Gagniere J, Deneuvy V, Deneuvy A, Roche G, Baudu E, Pereira B, Bonnet R, Barnich N, Carvalho FA, Pezet D, Bonnet M, Jalenques I. Preclinical and clinical evidence of the association of colibactin-producing Escherichia coli with anxiety and depression in colon cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(21): 2817-2826
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i21/2817.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i21.2817