Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2024; 30(21): 2817-2826
Published online Jun 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i21.2817
Published online Jun 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i21.2817
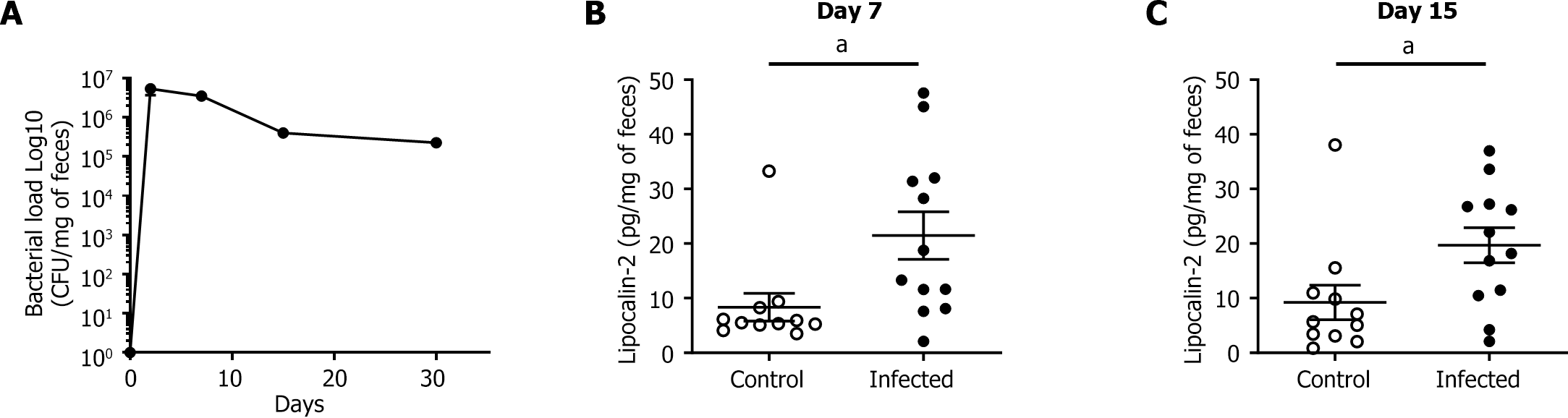
Figure 3 Chronic colibactin-producing Escherichia coli infection is associated with the induction of microinflammation.
A: Colonization of wild-type (WT) infected mice (n = 12) in the gastrointestinal tract followed by counting the fecal colony form units of colibactin-producing Escherichia coli (11G5 strain) at different time points. B and C: Colonic low-grade inflammation was assessed by measuring fecal lipocalin-2 levels at the peak of infection (7 DPI) and 15 DPI [WT control, n = 11 (stools could not be collected or analyzed for one mouse); WT infected mice, n = 12]. The white circles represent WT control mice, while the black circles represent WT infected mice. Statistical analysis: Student’s t test: aP < 0.05. CFU: Colony form unit.
- Citation: Rondepierre F, Meynier M, Gagniere J, Deneuvy V, Deneuvy A, Roche G, Baudu E, Pereira B, Bonnet R, Barnich N, Carvalho FA, Pezet D, Bonnet M, Jalenques I. Preclinical and clinical evidence of the association of colibactin-producing Escherichia coli with anxiety and depression in colon cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(21): 2817-2826
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i21/2817.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i21.2817