Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2024; 30(21): 2817-2826
Published online Jun 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i21.2817
Published online Jun 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i21.2817
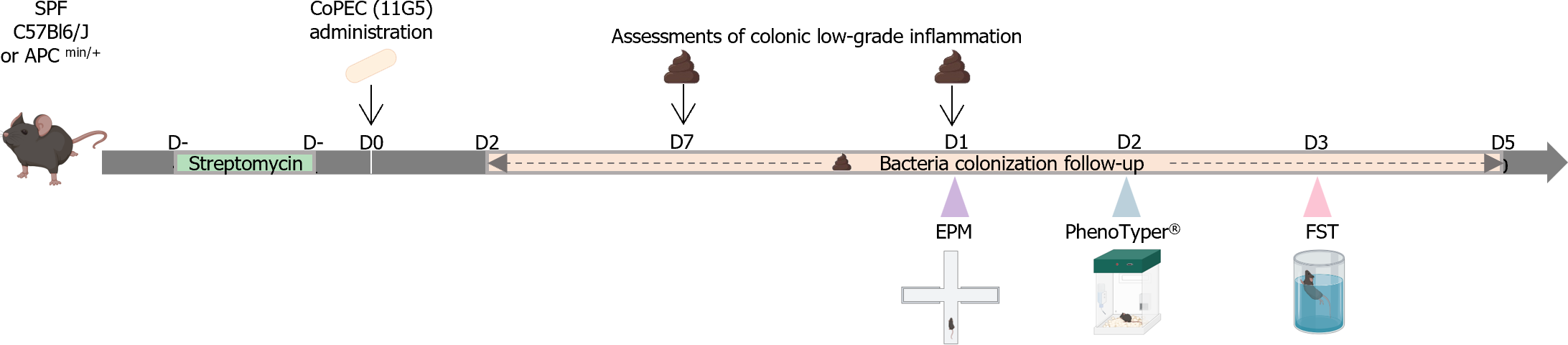
Figure 1 Experimental workflow of the preclinical models used in this study.
Wild-type or adenomatous polyposis colimultiple intestinal neoplasia/+ mice were chronically infected with the 11G5 CoPEC strain (109 bacteria per mouse) at D0 after pre-streptomycin treatment (from D-4 to D-1). Colonic low-grade inflammation was measured at D7 and D15. Elevated plus maze, Phenotyper and forced swimming test were performed at D15, D20 and D35 respectively. SPF: Specific pathogen free; CoPEC: Colibactin-producing Escherichia coli; EPM: Elevated plus maze; FST: Forced Swimming Test (Created with BioRender.com, Supplementary material).
- Citation: Rondepierre F, Meynier M, Gagniere J, Deneuvy V, Deneuvy A, Roche G, Baudu E, Pereira B, Bonnet R, Barnich N, Carvalho FA, Pezet D, Bonnet M, Jalenques I. Preclinical and clinical evidence of the association of colibactin-producing Escherichia coli with anxiety and depression in colon cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(21): 2817-2826
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i21/2817.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i21.2817