Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2024; 30(21): 2793-2816
Published online Jun 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i21.2793
Published online Jun 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i21.2793
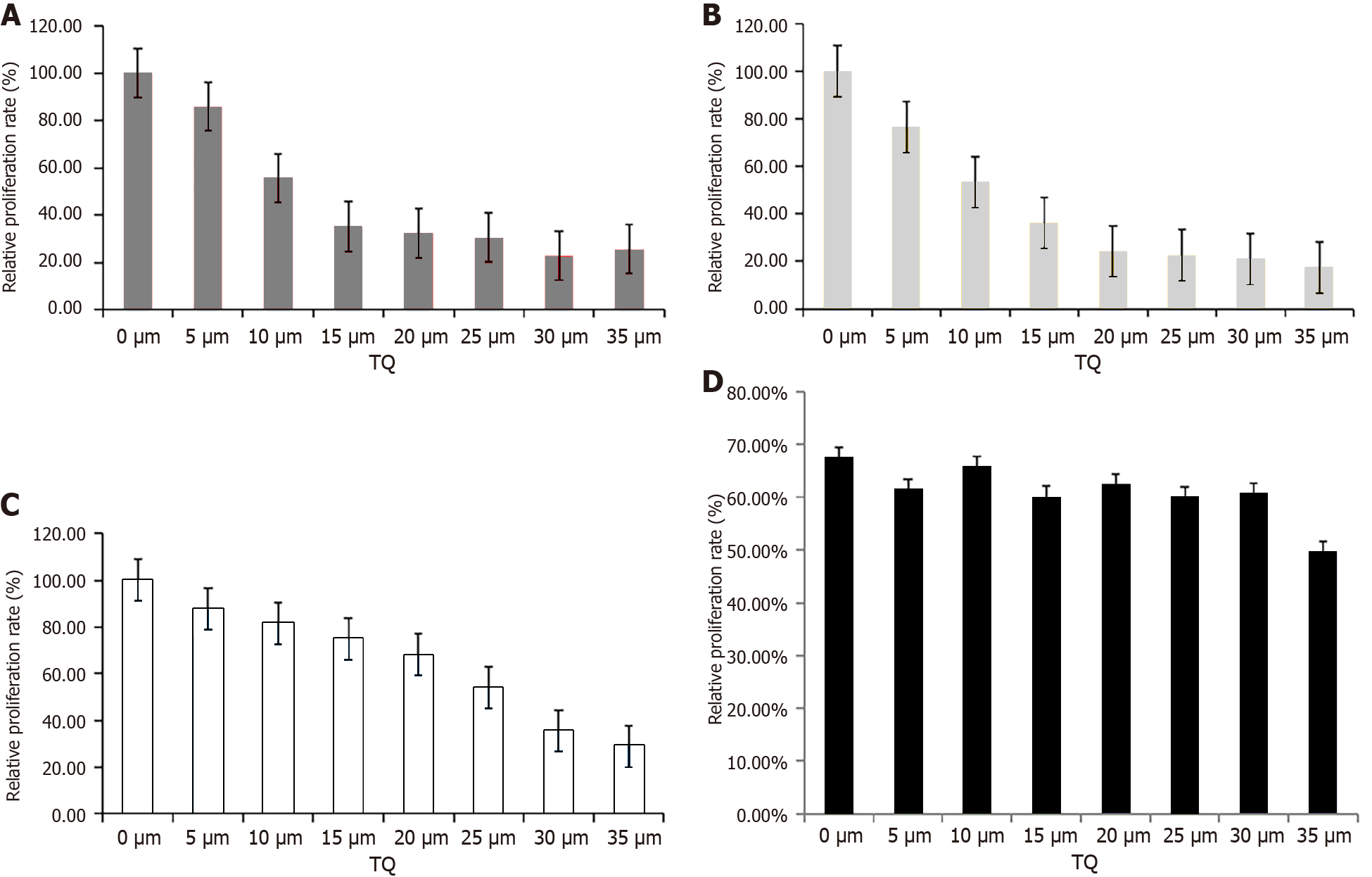
Figure 1 Cell counting kit-8 assay was performed to determine the effects of different concentrations of Thymoquinone on the proliferation rate of pancreatic cancer cells and pancreatic duct epithelial cells under hypoxia condition.
A: Cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) assay was performed to detect the effects of Thymoquinone (TQ) on the relative proliferation rate of PANC-1 cells under hypoxia condition; B: CCK-8 assay was performed to detect the effects of TQ on the relative proliferation rate of AsPC-1 cells under hypoxia condition; C: CCK-8 assay was performed to detect the effects of TQ on the relative proliferation rate of BxPC-3 cells under hypoxia condition; D: CCK-8 assay was performed to detect the effects of TQ on the relative proliferation rate of normal pancreatic duct epithelial cells under hypoxia condition. TQ: Thymoquinone.
- Citation: Zhao ZX, Li S, Liu LX. Thymoquinone affects hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression in pancreatic cancer cells via HSP90 and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(21): 2793-2816
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i21/2793.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i21.2793