Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2024; 30(20): 2689-2708
Published online May 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i20.2689
Published online May 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i20.2689
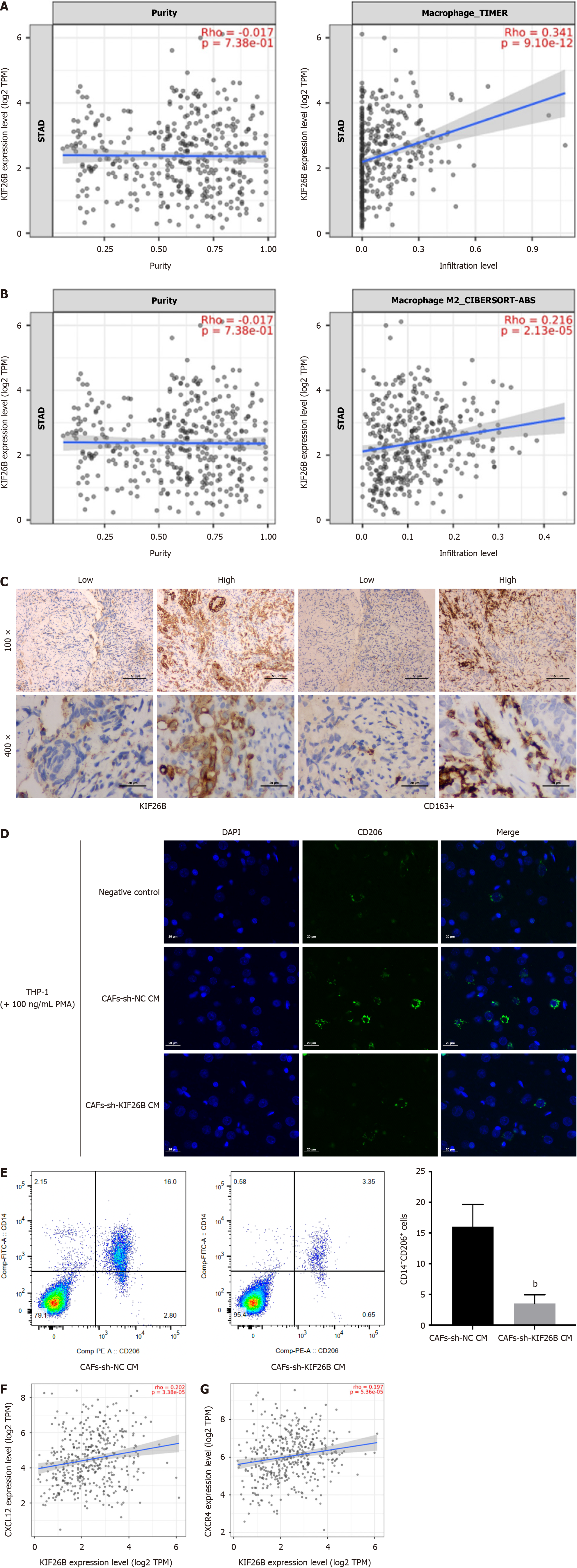
Figure 5 KIF26B enhances crosstalk between cancer-associated fibroblasts and macrophages, thereby mediating M2 polarization of macrophages.
A: Timer 2.0 analysis of the correlation between KIF26B expression and macrophage activation; B: Timer 2.0 analysis of the correlation between KIF26B expression and M2 type macrophages; C: The correlation between the expression of KIF26B and the level of CD163+ (M2 macrophage marker) infiltration was analyzed by immunohistochemistry. n = 3; D: Immunofluorescence detection of CD206 signaling in THP-1 cells. The supernatant of cancer-associated fibroblasts that transfected with sh-KIF26B was used to incubate THP-1 cells. n = 3; E: Flow cytometry was used to detect the number of M2-polarized macrophages. n = 3; F: Analyzing the correlation between KIF26B expression and chemokine CXCL12 expression through the Timer 2.0 database; G: Analyzing the correlation between KIF26B expression and CXCR4 expression trough the Timer 2.0 database. bP < 0.01. CAFs: Cancer-associated fibroblasts; sh-NC: sh-KIF26B negative controls.
- Citation: Huang LM, Zhang MJ. Kinesin 26B modulates M2 polarization of macrophage by activating cancer-associated fibroblasts to aggravate gastric cancer occurrence and metastasis. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(20): 2689-2708
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i20/2689.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i20.2689