Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2024; 30(20): 2689-2708
Published online May 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i20.2689
Published online May 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i20.2689
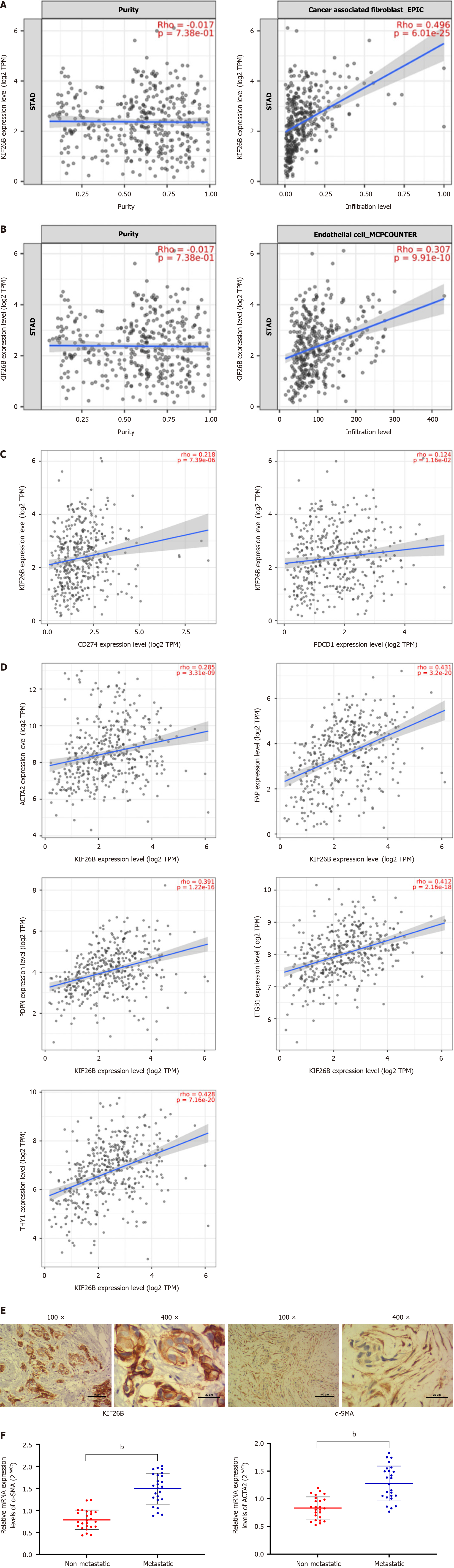
Figure 3 High expression of KIF26B may affect the activation or infiltration of gastric cancer related fibroblasts.
A: Timer 2.0 analysis of the correlation between KIF26B expression and the degree of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) infiltration; B: Timer 2.0 analysis of the correlation between KIF26B expression and the degree of cancer endothelial cell infiltration; C: Timer 2.0 analysis of the correlation between KIF26B expression and PD-1 (PDCD1), PD-L1 (CD274) expression; D: Timer 2.0 analysis to verify the correlation between KIF26B and CAFs biomarkers (ACTA2, FAP, ITGB1, PDPN, and THY1); E: Immunohistochemical analysis of KIF26B and α-SMA in gastric cancer (GC) tissues (n = 3); F: The mRNA levels of CAFs Biomarker α-SMA and ACTA2 in metastatic and non-metastatic GC tissues were detected by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (n = 25). bP < 0.01.
- Citation: Huang LM, Zhang MJ. Kinesin 26B modulates M2 polarization of macrophage by activating cancer-associated fibroblasts to aggravate gastric cancer occurrence and metastasis. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(20): 2689-2708
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i20/2689.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i20.2689