Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2024; 30(20): 2638-2656
Published online May 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i20.2638
Published online May 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i20.2638
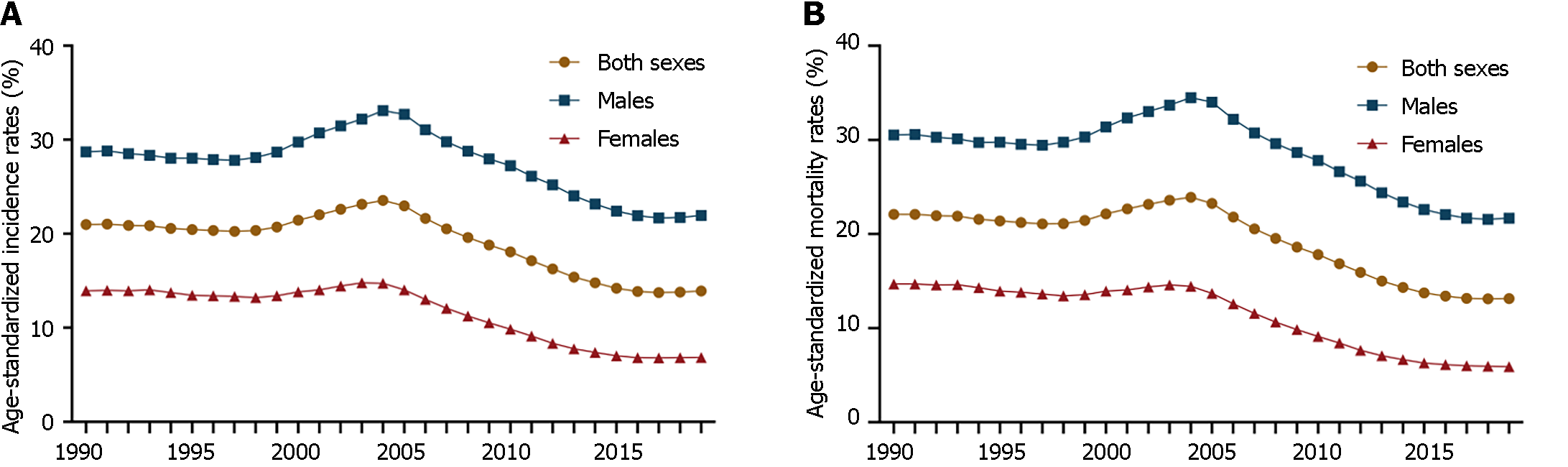
Figure 5 Trends in age-standardized incidence and mortality rates of esophageal cancer in China from 1990 to 2019, according to the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 database.
A: Trends in age-standardized incidence rates of esophageal cancer in China from 1990 to 2019, according to the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 (GBD 2019); B: Trends in age-standardized mortality rates of esophageal cancer in China from 1990 to 2019, according to the GBD 2019. Line charts show the trends in age-standardized incidence and mortality rates of esophageal cancer in China from 1990 to 2019 in both sexes, males and females, respectively. Source: Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation. Global Burden of Disease Collaborative Network, Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 Results, Seattle, United States: Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, 2020. Available from https://vizhub.healthdata.org/gbd-results/.
- Citation: Zhao YX, Zhao HP, Zhao MY, Yu Y, Qi X, Wang JH, Lv J. Latest insights into the global epidemiological features, screening, early diagnosis and prognosis prediction of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(20): 2638-2656
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i20/2638.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i20.2638