Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2024; 30(19): 2564-2574
Published online May 21, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i19.2564
Published online May 21, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i19.2564
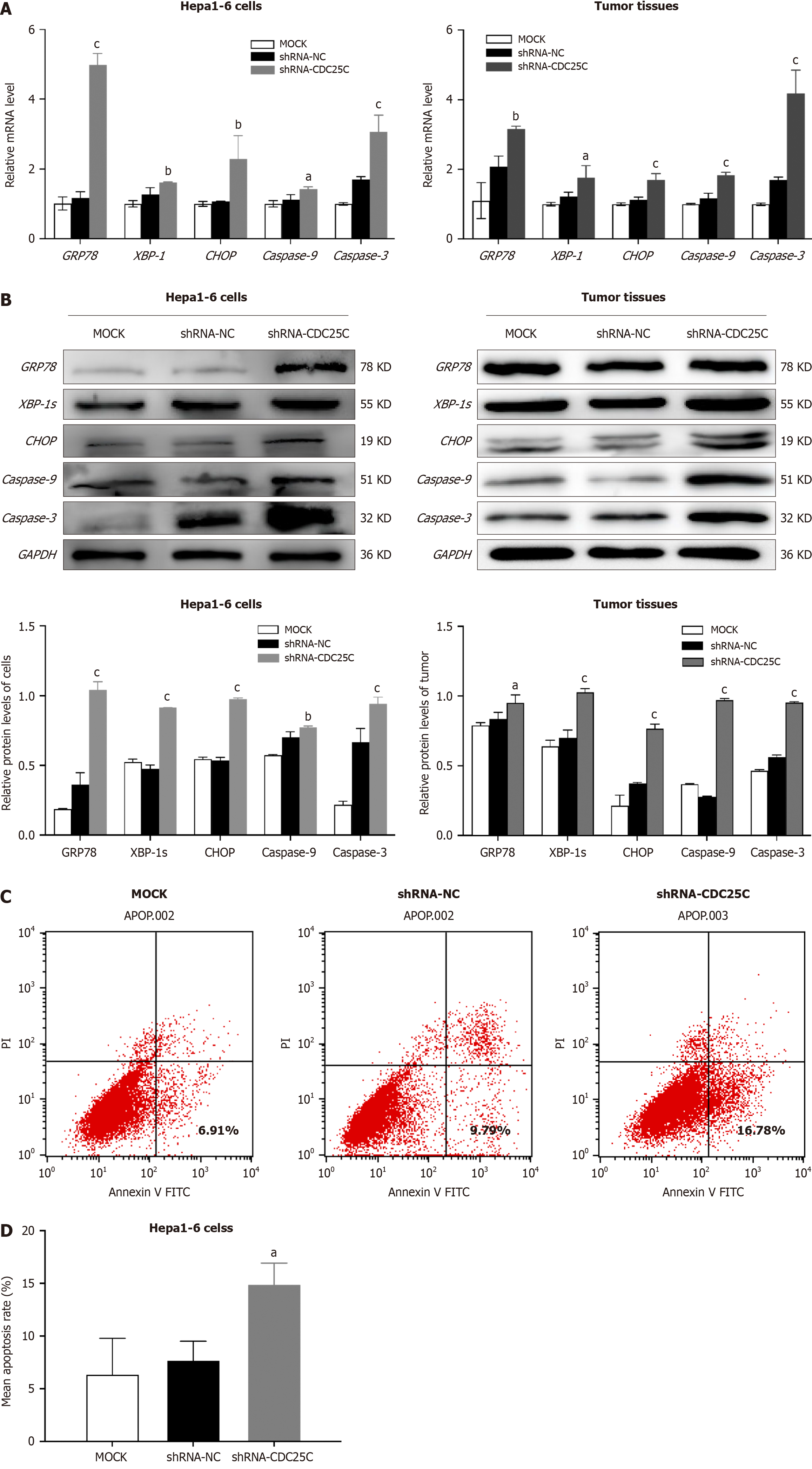
Figure 4 Cell division cyclin 25C knockdown induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and activated endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in Hepa1-6 cells and the corresponding xenograft tumors.
A and B: The expression of GRP78, XBP-1/s, CHOP, Caspase 9, and Caspase 3 in Hepa1-6 cells and the corresponding xenograft tumor tissues was analyzed at both the transcriptional and translational levels; C and D: The apoptosis rate of Hepa1-6 cells was assessed using flow cytometric analysis. The data represents the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. CDC25C: Cell division cyclin 25C; GRP78: Glucose-regulated protein 78; XBP-1: X-box binding protein-1; XBP-1s: Splicing of X-box binding protein-1; CHOP: C/EBP homologous protein.
- Citation: Li YF, Zheng FY, Miao XY, Liu HL, Zhang YY, Chao NX, Mo FR. Cell division cyclin 25C knockdown inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma development by inducing endoplasmic reticulum stress. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(19): 2564-2574
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i19/2564.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i19.2564