Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2024; 30(19): 2553-2563
Published online May 21, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i19.2553
Published online May 21, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i19.2553
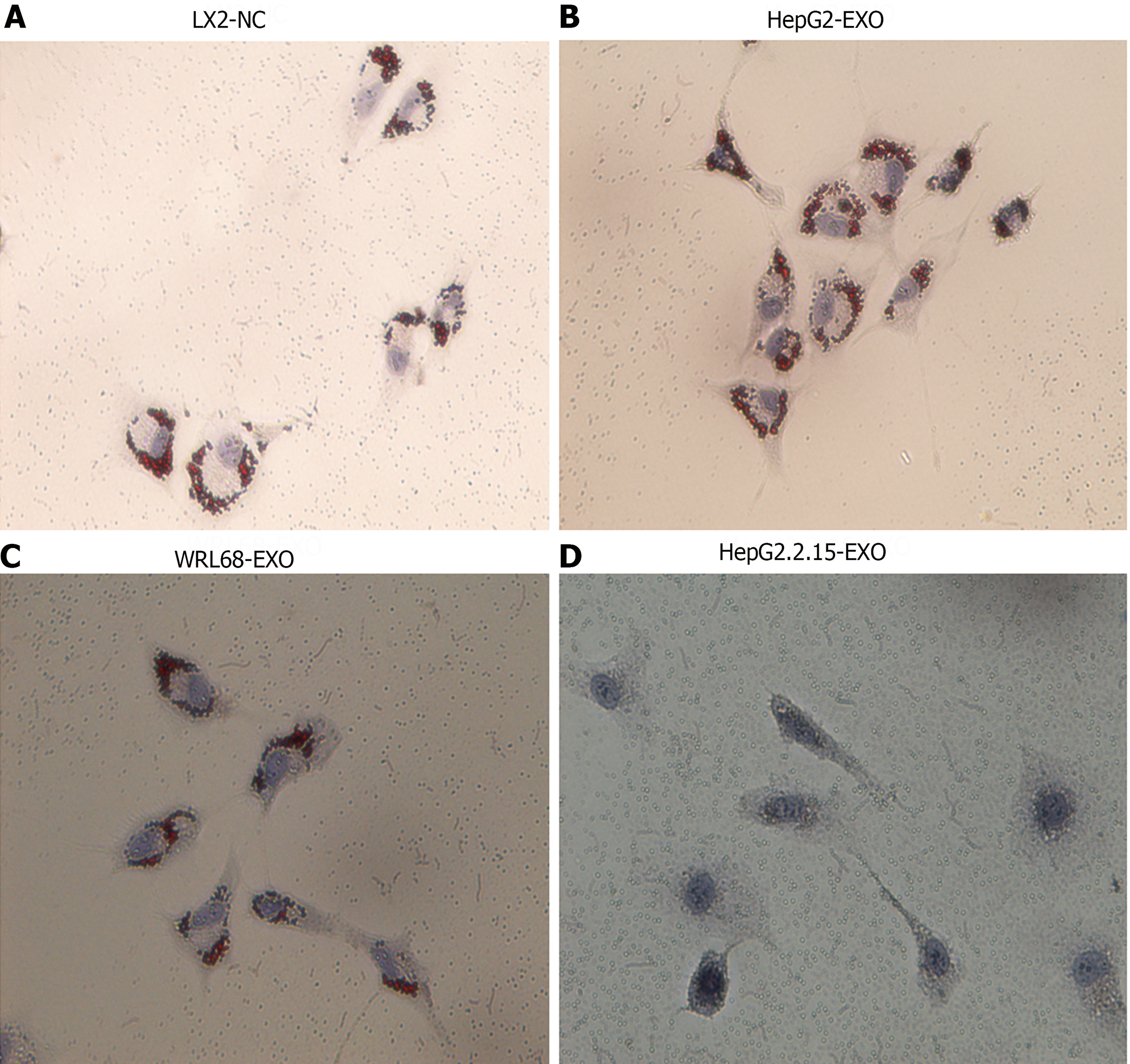
Figure 2 The impact of HepG2.
2.15-derived exosomes on the activation of LX2 cells. A: Display of LX2 cells in a normal culture environment, showing red lipid droplets; B: Illustration of LX2 cells co-cultured with HepG2-exo. Similar to the normal culture, red lipid droplets are present; C: Depiction of LX2 cells co-cultured with WRL68-exo. Also maintains presence of red lipid droplets; D: Representation of LX2 cells when co-cultured with HepG2.2.15-exo. Notably, after 24 h of oil red staining, the red lipid droplets disappear, indicating a significant change caused by the HepG2.2.15-exo. Magnification Times: 20 ×.
- Citation: Gao Y, Li L, Zhang SN, Mang YY, Zhang XB, Feng SM. HepG2.2.15-derived exosomes facilitate the activation and fibrosis of hepatic stellate cells. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(19): 2553-2563
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i19/2553.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i19.2553