Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2024; 30(16): 2184-2190
Published online Apr 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i16.2184
Published online Apr 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i16.2184
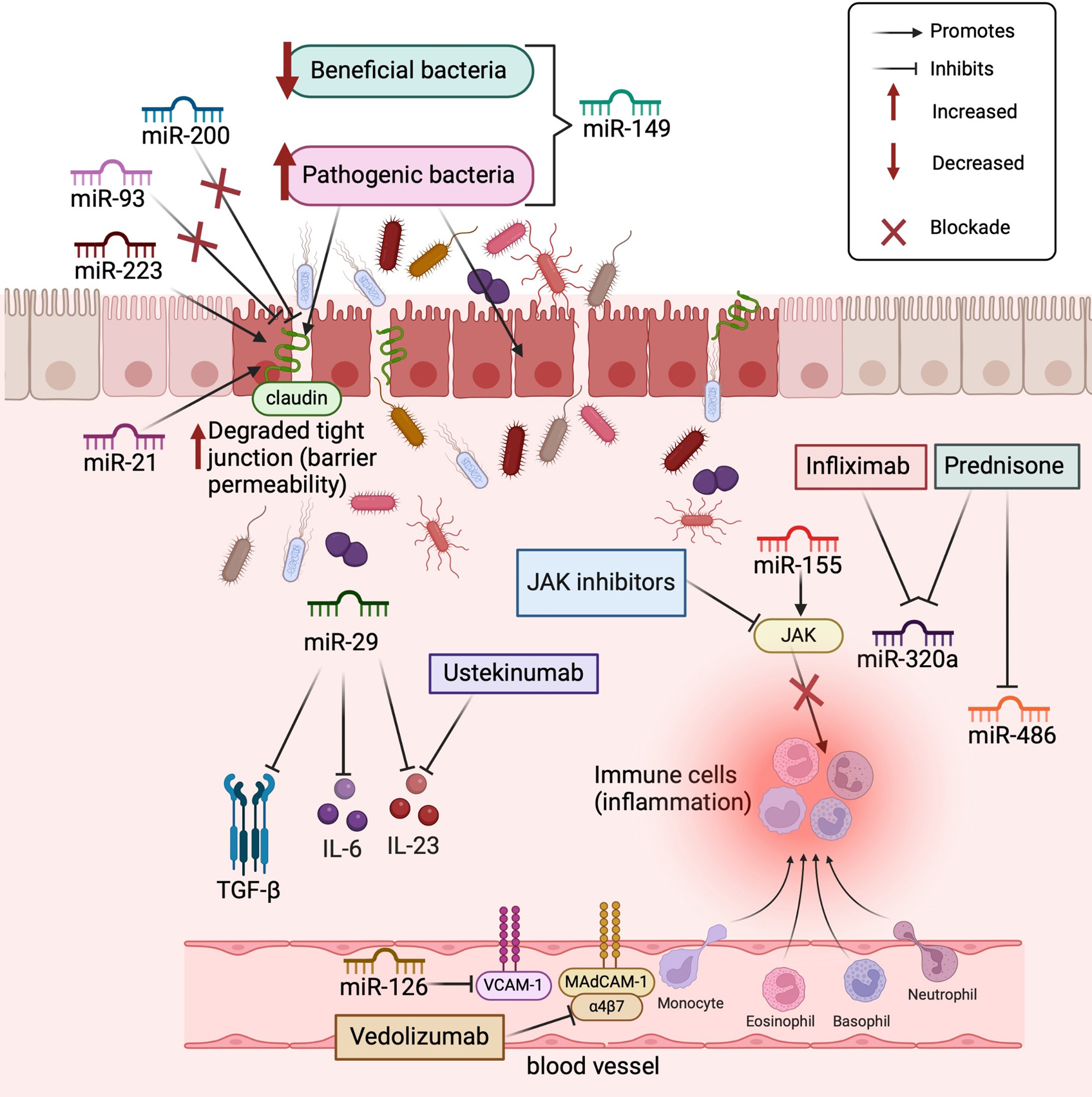
Figure 1 Main microRNAs involved in intestinal inflammation and inflammatory pathways targeted by medications used to treat inflammatory bowel disease.
MicroRNA (miR)-21 and miR-223 inhibit tight junctions, whereas miR-200 and miR-93 maintain tight junctions. miR-149 promotes changes in the intestinal microbiota, favoring the growth of pathogenic bacteria. Prednisone reduces miR-486 expression, while miR320a expression is reduced by prednisone and infliximab. miR-29 reduces the expression of transforming growth factor β, interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-23, similar to ustekinumab, a biological inhibitor of IL12/23. miR-155 regulates the activity of Janus kinase (JAK), which activates immune cells, whereas JAK inhibitors exert the opposite effects. miR126 regulates vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1), similar to vedolizumab, which regulates mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule-1 (MAdCAM-1). α4β7: Α4β7 integrin. Created with BioRender.com (Supplementary material).
- Citation: Oliveira ECS, Quaglio AEV, Grillo TG, Di Stasi LC, Sassaki LY. MicroRNAs in inflammatory bowel disease: What do we know and what can we expect? World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(16): 2184-2190
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i16/2184.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i16.2184