Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2024; 30(15): 2155-2174
Published online Apr 21, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i15.2155
Published online Apr 21, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i15.2155
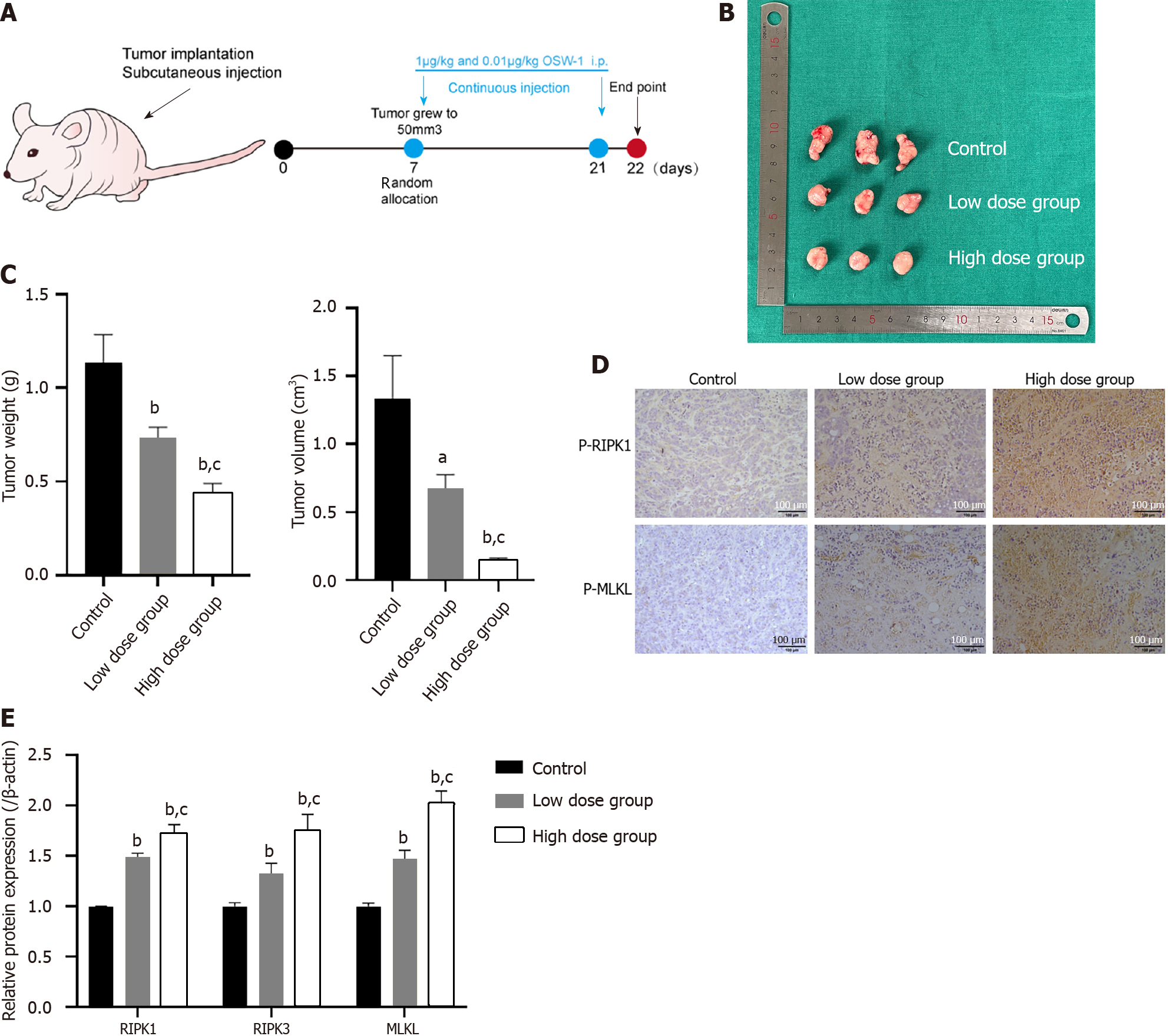
Figure 7 The inhibition of colorectal cancer cell proliferation is associated with necroptosis induced by OSW-1 in vivo.
A: Treatment schedule for mice intravenously injected with 5 × 106 HT29 cells; B: Images of the harvested subcutaneous tumors. Tumor growth in the OSW-1 group was markedly suppressed compared to that in the control group; C: The tumor volume (mm3) and weight in the high-dose OSW-1 group were lower than those in the low-dose group; D: Immunohistochemistry staining of p-RIPK1 and p-MLKL in xenograft nude mice (magnification, 200 ×); E: In xenograft nude mouse models, the expression levels of RIPK1, RIPK3 and MLKL in the high-dose group were increased in comparison to the low-dose group. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01 vs Control, cP < 0.05 and dP < 0.01 vs Low dose group.
- Citation: Wang N, Li CY, Yao TF, Kang XD, Guo HS. OSW-1 triggers necroptosis in colorectal cancer cells through the RIPK1/RIPK3/MLKL signaling pathway facilitated by the RIPK1-p62/SQSTM1 complex. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(15): 2155-2174
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i15/2155.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i15.2155